Anaemia associated with chemotherapy
Active Ingredient: Epoetin zeta
Indication for Epoetin zeta
Epoetin zeta is indicated in adults receiving chemotherapy for solid tumours, malignant lymphoma or multiple myeloma, and at risk of transfusion as assessed by the patient’s general status (e.g. cardiovascular status, pre-existing anaemia at the start of chemotherapy) for the treatment of anaemia and reduction of transfusion requirements.
For this indication, competent medicine agencies globally authorize below treatments:
150 IU/kg once every 2 days
Route of admnistration
Subcutaneous
Defined daily dose
150 - 150 [iU] per kg of body weight
Dosage regimen
From 150 To 150 [iU] per kg of body weight once every 2 day(s)
Detailed description
Anaemia symptoms and sequelae may vary with age, gender, and overall burden of disease; a physician’s evaluation of the individual patient ́s clinical course and condition is necessary.
Epoetin zeta should be administered to patients with anaemia (e.g. haemoglobin concentration ≤10 g/dL [6.2 mmol/L]).
The initial dose is 150 IU/kg subcutaneously, 3 times per week.
Alternatively, epoetin zeta can be administered at an initial dose of 450 IU/kg subcutaneously once weekly.
Appropriate adjustment of the dose should be made in order to maintain haemoglobin concentrations within the desired concentration range between 10 g/dL to 12 g/dL (6.2 to 7.5 mmol/L).
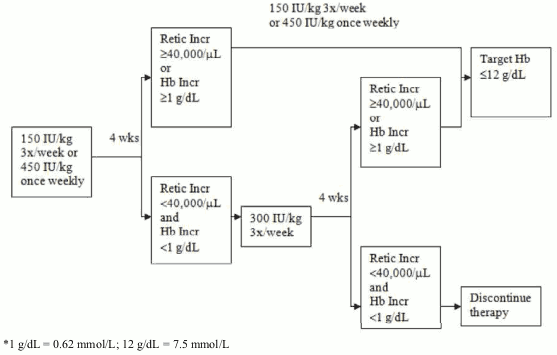
Due to intra-patient variability, occasional individual haemoglobin concentrations for a patient above and below the desired haemoglobin concentration range may be observed. Haemoglobin variability should be addressed through dose management, with consideration for the desired haemoglobin concentration range between 10 g/dL (6.2 mmol/L) to 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L). A sustained haemoglobin concentration of greater than 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) should be avoided; guidance for appropriate dose adjustment for when haemoglobin concentrations exceed 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) are described below. If the haemoglobin concentration has increased by at least 1 g/dL (0.62 mmol/L) or the reticulocyte count has increased ≥40,000 cells/μL above baseline after 4 weeks of treatment, the dose should remain at 150 IU/kg 3 times per week or 450 IU/kg once weekly. If the haemoglobin concentration increase is <1 g/dL (<0.62 mmol/L) and the reticulocyte count has increased <40 000 cells/μl above baseline, increase the dose to 300 IU/kg 3 times per week. If after an additional 4 weeks of therapy at 300 IU/kg 3 times per week, the haemoglobin concentration has increased ≥1 g/dL (≥0.62 mmol/L) or the reticulocyte count has increased ≥40 000 cells/μl, the dose should remain at 300 IU/kg 3 times per week. If the haemoglobin concentration has increased <1 g/dL (<0.62 mmol/L) and the reticulocyte count has increased <40 000 cells/μL above baseline, response is unlikely and treatment should be discontinued.
Dose adjustment to maintain haemoglobin concentrations between 10 g/dL to 12 g/dL (6.2 to 7.5 mmol/L)
If the haemoglobin concentration is increasing by more than 2 g/dL (1.25 mmol/L) per month, or if the haemoglobin concentration level exceeds 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L), reduce the epoetin zeta dose by about 25 to 50%.
If the haemoglobin concentration level exceeds 13 g/dL (8.1 mmol/L), discontinue therapy until it falls below 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) and then reinitiate epoetin zeta therapy at a dose 25% below the previous dose.
The recommended dosing regimen is described in the following diagram*:
Patients should be monitored closely to ensure that the lowest approved dose of ESA is used to provide adequate control of the symptoms of anaemia.
Epoetin zeta therapy should continue until one month after the end of chemotherapy.
Dosage considerations
The injections should be given in the limbs or the anterior abdominal wall.
450 IU/kg once every week
Route of admnistration
Subcutaneous
Defined daily dose
450 - 450 [iU] per kg of body weight
Dosage regimen
From 450 To 450 [iU] per kg of body weight once every 7 day(s)
Detailed description
Anaemia symptoms and sequelae may vary with age, gender, and overall burden of disease; a physician ́s evaluation of the individual patient ́s clinical course and condition is necessary.
Epoetin zeta should be administered to patients with anaemia (e.g. haemoglobin concentration ≤10 g/dL [6.2 mmol/L]).
The initial dose is 150 IU/kg subcutaneously, 3 times per week.
Alternatively, epoetin zeta can be administered at an initial dose of 450 IU/kg subcutaneously once weekly.
Appropriate adjustment of the dose should be made in order to maintain haemoglobin concentrations within the desired concentration range between 10 g/dL to 12 g/dL (6.2 to 7.5 mmol/L).
Due to intra-patient variability, occasional individual haemoglobin concentrations for a patient above and below the desired haemoglobin concentration range may be observed. Haemoglobin variability should be addressed through dose management, with consideration for the desired haemoglobin concentration range between 10 g/dL (6.2 mmol/L) to 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L). A sustained haemoglobin concentration of greater than 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) should be avoided; guidance for appropriate dose adjustment for when haemoglobin concentrations exceed 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) are described below. If the haemoglobin concentration has increased by at least 1 g/dL (0.62 mmol/L) or the reticulocyte count has increased ≥ 40 000 cells/μL above baseline after 4 weeks of treatment, the dose should remain at 150 IU/kg 3 times per week or 450 IU/kg once weekly. If the haemoglobin concentration increase is <1 g/dL (<0.62 mmol/L) and the reticulocyte count has increased <40 000 cells/μl above baseline, increase the dose to 300 IU/kg 3 times per week. If after an additional 4 weeks of therapy at 300 IU/kg 3 times per week, the haemoglobin concentration has increased ≥ 1 g/dL (≥0.62 mmol/L) or the reticulocyte count has increased ≥40 000 cells/μl, the dose should remain at 300 IU/kg 3 times per week. If the haemoglobin concentration has increased <1 g/dL (<0.62 mmol/L) and the reticulocyte count has increased <40 000 cells/μL above baseline, response is unlikely and treatment should be discontinued.
Dose adjustment to maintain haemoglobin concentrations between 10 g/dL to 12 g/dL (6.2 to 7.5 mmol/L)
If the haemoglobin concentration is increasing by more than 2 g/dL (1.25 mmol/L) per month, or if the haemoglobin concentration level exceeds 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L), reduce the epoetin zeta dose by about 25 to 50%.
If the haemoglobin concentration level exceeds 13 g/dL (8.1 mmol/L), discontinue therapy until it falls below 12 g/dL (7.5 mmol/L) and then reinitiate epoetin zeta therapy at a dose 25% below the previous dose.
The recommended dosing regimen is described in the following diagram*:
Patients should be monitored closely to ensure that the lowest approved dose of ESA is used to provide adequate control of the symptoms of anaemia.
Epoetin zeta therapy should continue until one month after the end of chemotherapy.
Dosage considerations
The injections should be given in the limbs or the anterior abdominal wall.
Liability Disclaimer : RxReasoner has utilized reasonable care in providing content and services that are accurate, complete and up to date. However, RxReasoner does not accept any responsibility or liability about it. The content and services of RxReasoner are for informational purposes only and they are not intended to be a substitute for the knowledge, expertise, skill, and judgment of physicians, pharmacists, nurses, or other healthcare professionals involved in patient care. RxReasoner offers no medical advice. Users are responsible for the use of the provided content. A shown indication or treatment should not be construed to indicate that the medication is safe, appropriate, or effective in any given patient or under any particular circumstances. The absence of an indication or treatment should not roule out the existence of other appropriate medications. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or medicament. RxReasoner is not liable for any damages allegedly sustained arising out of the use of its content and services.