ADREVIEW Solution for injection Ref.[10310] Active ingredients: Iobenguane ¹²³I
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2020
1. Indications and Usage
1.1 Pheochromocytoma and Neuroblastoma
AdreView is a radiopharmaceutical indicated for use in the detection of primary or metastatic pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma as an adjunct to other diagnostic tests.
1.2 Congestive Heart Failure
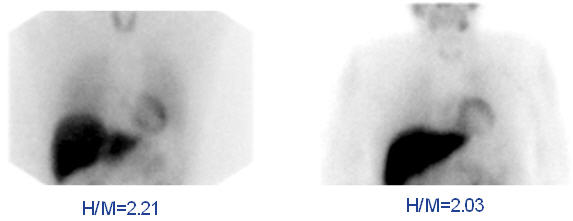
AdreView is indicated for scintigraphic assessment of sympathetic innervation of the myocardium by measurement of the heart to mediastinum (H/M) ratio of radioactivity uptake in patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II or class III heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤35%. Among these patients, AdreView may be used to help identify patients with lower one and two year mortality risks, as indicated by an H/M ratio ≥1.6.
Limitations of Use: In patients with congestive heart failure, AdreView utility has not been established for:
- selecting a therapeutic intervention or for monitoring the response to therapy;
- using the H/M ratio to identify a patient with a high risk for death.
2. Dosage and Administration
2.1 Radiation Safety
AdreView emits radiation and must be handled with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to clinical personnel and patients. Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides. AdreView dosing is based upon the radioactivity determined using a suitable calibration system immediately prior to administration.
To minimize radiation dose to the bladder, prior to and following AdreView administration, encourage hydration to permit frequent voiding. Encourage the patient to void frequently for the first 48 hours following AdreView administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
2.2 Thyroid Blockade
Before administration of AdreView to patients at risk for thyroid accumulation of the drug, administer Potassium Iodide Oral Solution or Lugol’s Solution (equivalent to 100 mg iodide for adults, body-weight adjusted for children) or potassium perchlorate (400 mg for adults, body-weight adjusted for children) to block uptake of iodine 123 by the patient’s thyroid. Administer the blocking agent at least one hour before the dose of AdreView [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Individualize thyroid blockade; for example, the blockade may not be necessary for patients who have undergone thyroidectomy or those with a very limited life expectancy.
2.3 Preparation and Administration
- Assess pregnancy status before administering AdreView to a female of reproductive potential.
- Inspect the AdreView vial for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Use aseptic procedures and a radiation shielding syringe during administration. Administer the dose as an intravenous injection over 1 to 2 minutes. A subsequent injection of 0.9% sodium chloride may be used to ensure full delivery of the dose.
2.4 Recommended Dose for Adults
For adults (≥16 years of age), the recommended dose is 10 mCi (370 MBq) [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2)].
2.5 Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients
For pediatric patients <16 years of age weighing ≥70 kg, the recommended dose is 10 mCi (370 MBq) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
For pediatric patients <16 years of age weighing <70 kg, the recommended dose should be calculated according to patient body weight as shown in Table 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The benzyl alcohol in AdreView may cause serious adverse reactions in premature or low birth-weight infants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Table 1. AdreView Dose Preparation for Pediatric Patients*:
| Weight (kg) | Fraction of adult activity | AdreView (mCi) pediatric dose | AdreView (MBq) pediatric dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.1 | 1 | 37 |
| 4 | 0.14 | 1.4 | 52 |
| 6 | 0.19 | 1.9 | 70 |
| 8 | 0.23 | 2.3 | 85.1 |
| 10 | 0.27 | 2.7 | 99.9 |
| 12 | 0.32 | 3.2 | 118.4 |
| 14 | 0.36 | 3.6 | 133.2 |
| 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 148 |
| 18 | 0.44 | 4.4 | 162.8 |
| 20 | 0.46 | 4.6 | 170.2 |
| 22 | 0.5 | 5 | 185 |
| 24 | 0.53 | 5.3 | 196.1 |
| 26 | 0.56 | 5.6 | 207.2 |
| 28 | 0.58 | 5.8 | 214.6 |
| 30 | 0.62 | 6.2 | 229.4 |
| 32 | 0.65 | 6.5 | 240.5 |
| 34 | 0.68 | 6.8 | 251.6 |
| 36 | 0.71 | 7.1 | 262.7 |
| 38 | 0.73 | 7.3 | 270.1 |
| 40 | 0.76 | 7.6 | 281.2 |
| 42 | 0.78 | 7.8 | 288.6 |
| 44 | 0.8 | 8 | 296 |
| 46 | 0.82 | 8.2 | 303.4 |
| 48 | 0.85 | 8.5 | 314.5 |
| 50 | 0.88 | 8.8 | 325.6 |
| 52 | 0.9 | 9 | 333 |
| 54 | 0.9 | 9 | 333 |
| 56 | 0.92 | 9.2 | 340.4 |
| 58 | 0.92 | 9.2 | 340.4 |
| 60 | 0.96 | 9.6 | 355.2 |
| 62 | 0.96 | 9.6 | 355.2 |
| 64 | 0.98 | 9.8 | 362.6 |
| 66 | 0.98 | 9.8 | 362.6 |
| 68 | 0.99 | 9.9 | 366.3 |
* Based on a reference activity for an adult scaled to body weight according to the schedule proposed by the European Association of Nuclear Medicine Paediatric Task Group.
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to adults and children from intravenous administration of AdreView are as shown in Table 2:
Table 2. Estimated Absorbed Radiation Dose from AdreView:
| ORGAN / TISSUE | ABSORBED DOSE PER UNIT ADMINISTERED ACTIVITY | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADULT | 15-YEAR OLD | 10-YEAR OLD | 5-YEAR OLD | 1-YEAR OLD | NEONATES | |||||||||
| μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | μGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | |||
| Adrenals | 16 | 0.059 | 21 | 0.078 | 31 | 0.115 | 42 | 0.155 | 67 | 0.248 | 111 | 0.411 | ||
| Brain | 3.9 | 0.014 | 4.9 | 0.018 | 8.1 | 0.030 | 13 | 0.048 | 24 | 0.089 | 55.9 | 0.207 | ||
| Breast | 4.7 | 0.017 | 5.9 | 0.022 | 9.4 | 0.035 | 15 | 0.056 | 28 | 0.104 | 65.3 | 0.242 | ||
| Gallbladder | 20 | 0.074 | 24 | 0.089 | 34 | 0.126 | 51 | 0.189 | 95 | 0.352 | 200 | 0.740 | ||
| GI Tract | Stomach Wall | 7.6 | 0.028 | 10 | 0.037 | 17 | 0.063 | 27 | 0.100 | 51 | 0.189 | 114 | 0.422 | |
| Small Intestine Wall | 7.7 | 0.028 | 9.8 | 0.036 | 16 | 0.059 | 25 | 0.093 | 46 | 0.170 | 104 | 0.385 | ||
| Colon Wall | 8.1 | 0.030 | 10 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 26 | 0.096 | 46 | 0.170 | 104.3 | 0.386 | ||
| Upper Large Intestine Wall | 8.4 | 0.031 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 30 | 0.111 | 53 | 0.196 | 119 | 0.440 | ||
| Lower Large Intestine Wall | 7.7 | 0.028 | 9.6 | 0.036 | 15 | 0.056 | 21 | 0.078 | 38 | 0.141 | 84.9 | 0.314 | ||
| Heart Wall | 18 | 0.067 | 23 | 0.085 | 35 | 0.130 | 53 | 0.196 | 94 | 0.348 | 182 | 0.673 | ||
| Kidneys | 13 | 0.048 | 16 | 0.059 | 24 | 0.089 | 35 | 0.130 | 59 | 0.218 | 132 | 0.488 | ||
| Liver | 67 | 0.248 | 87 | 0.322 | 130 | 0.481 | 180 | 0.666 | 330 | 1.221 | 720 | 2.664 | ||
| Lungs | 16 | 0.059 | 23 | 0.085 | 32 | 0.118 | 48 | 0.178 | 89 | 0.329 | 215 | 0.796 | ||
| Muscles | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 12 | 0.044 | 17 | 0.063 | 33 | 0.122 | 75.1 | 0.278 | ||
| Esophagus | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 32 | 0.118 | 72.2 | 0.267 | ||
| Osteogenic Cells | 16 | 0.059 | 21 | 0.078 | 31 | 0.115 | 47 | 0.174 | 100 | 0.370 | 254 | 0.940 | ||
| Ovaries | 7.9 | 0.029 | 10 | 0.037 | 15 | 0.056 | 22 | 0.081 | 41 | 0.152 | 92.3 | 0.342 | ||
| Pancreas | 12 | 0.044 | 15 | 0.056 | 25 | 0.093 | 39 | 0.144 | 68 | 0.252 | 143 | 0.529 | ||
| Red marrow | 5.6 | 0.021 | 6.8 | 0.025 | 10 | 0.037 | 15 | 0.056 | 30 | 0.111 | 89.5 | 0.331 | ||
| Skin | 3.7 | 0.014 | 4.4 | 0.016 | 7.1 | 0.026 | 11 | 0.041 | 21 | 0.078 | 53.1 | 0.196 | ||
| Spleen | 20 | 0.074 | 27 | 0.100 | 42 | 0.155 | 64 | 0.237 | 110 | 0.407 | 282 | 1.043 | ||
| Testes | 5.4 | 0.020 | 7.1 | 0.026 | 11 | 0.041 | 16 | 0.059 | 30 | 0.111 | 69.9 | 0.259 | ||
| Thymus | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 32 | 0.118 | 72.2 | 0.267 | ||
| Thyroid | 4.7 | 0.017 | 6.1 | 0.023 | 9.9 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 30 | 0.111 | 69.4 | 0.257 | ||
| Urinary Bladder Wall | 66 | 0.244 | 84 | 0.311 | 110 | 0.407 | 110 | 0.407 | 200 | 0.740 | 478.0 | 1.769 | ||
| Uterus | 11 | 0.041 | 14 | 0.052 | 21 | 0.078 | 28 | 0.104 | 51 | 0.189 | 110.0 | 0.407 | ||
| Whole Body | 8.1 | 0.030 | 10 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 24 | 0.089 | 44 | 0.163 | 104.0 | 0.385 | ||
| EFFECTIVE DOSE | µSv/MBq | 13.7 | 18.1 | 26.7 | 37.6 | 68 | 162 | |||||||
| mSv/mCi | 0.507 | 0.670 | 0.988 | 1.39 | 2.52 | 6 | ||||||||
* OLINDA/EXM calculation based on biodistribution data from Swanson et al. and Publication 53 of the ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) [Annals of the ICRP 1987; 18 (1-4): 329-331]
The effective dose resulting from an administered activity amount of 10 mCi is 5.07 mSv in an adult.
2.7 Imaging Guidelines
Pheochromocytoma and Neuroblastoma
Begin whole body planar scintigraphy imaging 24 ± 6 hours following administration of AdreView. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) may be performed following planar scintigraphy, as appropriate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Congestive Heart Failure
Begin anterior planar imaging of the chest at 4 hours (± 10 minutes) following administration of AdreView. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) can then be performed. The recommended collimator for all imaging is a low-energy high-resolution. The recommended matrix for planar images is 128×128. The camera should be positioned to include the entire heart and as much of the upper chest as possible within the field of view [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2.8 Estimation of the H/M Ratio among Patients with Congestive Heart Failure
Initial evaluation of cardiac AdreView images involves visual examination of the location, pattern and intensity of cardiac radioactivity uptake to guide quantitative assessment (see Step 1 below). Perform quantitative assessment of radioactivity uptake in terms of the heart/mediastinum ratio (H/M) on anterior planar images of the chest (see Step 2 below).
Step 1. Visual Guidelines for AdreView Cardiac Uptake on Anterior Planar Chest Images
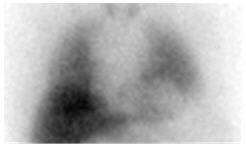
- a. Normal:
Distinct visualization of the left ventricular myocardium in the left lower chest, with greater uptake in the heart than in the adjacent lungs and mediastinum (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Normal anterior planar AdreView image of the chest:
- b. Abnormal:
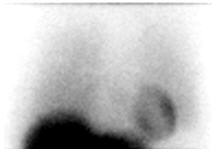
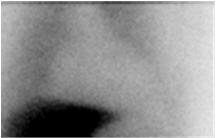
Homogeneously or heterogeneously decreased cardiac uptake, with indistinct or absent visualization of the left ventricular myocardium. Cardiac activity is usually less than or equal to that of the adjacent left lung (Figure 2a). In extreme cases, little or no AdreView uptake is seen in the left lower chest (Figure 2b).
Figure 2. Abnormal anterior planar AdreView images of the chest: a) Heterogeneously reduced cardiac uptake; b) Absent cardiac uptake:
Figure 2a:
Figure 2b:
Step 2. Quantitate AdreView Cardiac Uptake
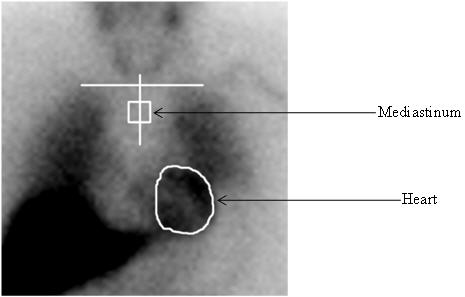
The AdreView H/M ratio is determined from the activity in heart (H) and mediastinum (M) regions of interest (ROIs) drawn on the anterior planar chest image (Figure 3) using the following procedure:
- Draw an irregular ROI defining the epicardial border of the heart. If the epicardial border cannot be defined because all or the majority of the myocardium is not visualized, draw the ROI based upon the presumed location of the heart, using the medial aspects of the left and right lower lung for anatomical guidance.
- Draw a horizontal line to mark the estimated location of the lung apices. If the most superior aspect of the image does not include the lung apices (because of limited field of view for a small gamma camera), draw this line at the top of the image display.
- Draw a vertical line approximately equidistant from the medial aspects of the right and left lung.
- Examine the counts for the 12 pixels along the vertical line starting 4 pixels below the intersection point with the horizontal line determined in step 2, and identify the pixel with the lowest counts. If more than one pixel has this same number of counts, choose the most superiorly located pixel.
- Using the pixel defined in step 4 as the center, draw a square ROI of 7×7 dimensions.
- Calculate the H/M ratio by dividing the counts/pixel in the total myocardium ROI determined in step 1 by the counts/pixel in the 7×7 pixel mediastinal ROI determined in step 5.
Figure 3. Illustration of creation of regions of interest for determination of the H/M ratio:
2.8.105 SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Step 3. Interpretation of AdreView H/M Ratio
The expected range for AdreView H/M ratio is 1.0 to 2.4 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Figure 4. Examples of AdreView Images in Subjects with Lower One and Two Year Mortality Risk:
10. Overdosage
The major manifestations of overdose relate predominantly to increased radiation exposure, with the long term risks for neoplasia.
16.2. Storage and Handling
Storage
Store AdreView at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP]. This product does not contain a preservative. Store within the original lead container or equivalent radiation shielding.
In accordance with USP recommendations Iobenguane I 123 Injection preparations should not be used after the expiration date and time stated on the label.
Handling
This preparation is approved for use by persons licensed by the Illinois Emergency Management Agency pursuant to 32 IL. Adm. Code Section 330.260(a) and 335.4010 or equivalent licenses of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission or an Agreement State.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.