BENZYLPENICILLIN SODIUM Powder for injection Ref.[6457] Active ingredients: Benzylpenicillin
Source: Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (GB) Revision Year: 2016 Publisher: Genus Pharmaceuticals, Linthwaite, Huddersfield, HD7 5QH, UK
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Beta-lactamase sensitive penicillins
ATC code: J01CE01
General Properties
Benzylpenicillin sodium is a beta-lactam antibiotic. It is bacteriocidal by inhibiting bacterial cell wall biosynthesis.
Breakpoints
The tentative breakpoints (British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, BSAC) for benzylpenicillin sodium are as follows:
| Organism | S ≤ (mg/L) | I (mg/L) | R ≥ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 0.06 | 0.12-1.0 | 2.0 |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | |||
| Neisseria meningitides | 0.06 | 0.12 | |
| Haemolytic streptococci | 0.12 | 0.25 | |
| Staphylococci | |||
| Moraxella catarrhalis | |||
| Haemophilus influenzae | |||
| Rapidly growing anaerobes | 1.0 | 2.0 |
S = Susceptible, I = Intermediate susceptibility, R = Resistant
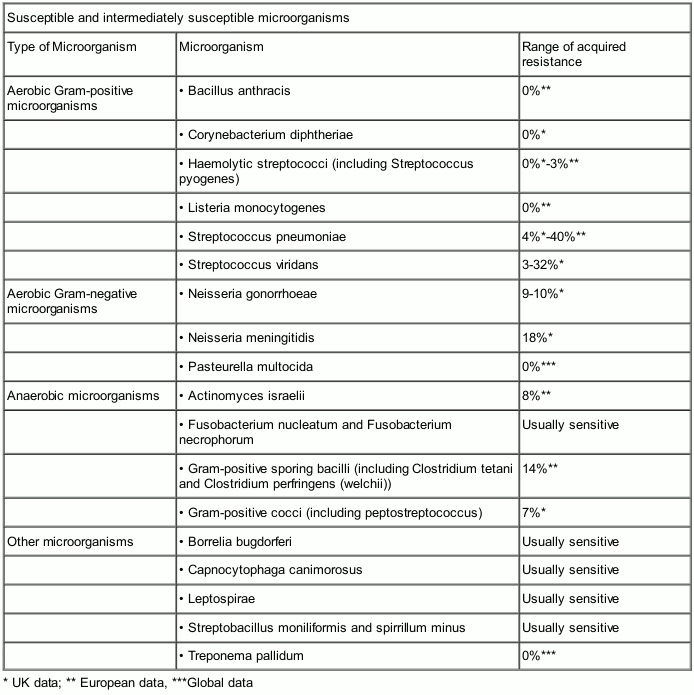
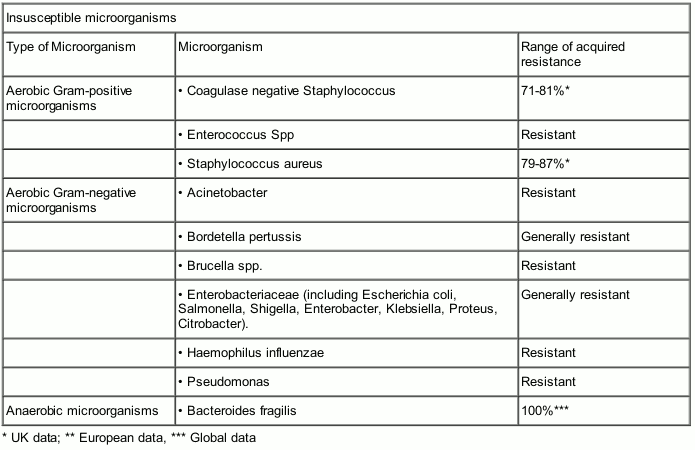
Susceptibility
The prevalence of resistance may vary geographically and with time for selected species and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. The following table gives only approximate guidance on probabilities whether microorganisms will be susceptible to benzylpenicillin sodium or not.
Other Information
Known Resistance Mechanisms and Cross-resistance
Penicillin resistance can be mediated by alteration of penicillin binding proteins or development of beta-lactamases.
Resistance to penicillin may be associated with cross-resistance to a variety of other beta lactam antibiotics either due to a shared target site that is altered, or due to a beta-lactamase with a broad range of substrate molecules. In addition to this, cross resistance to unrelated antibiotics can develop due to more than one resistance gene being present on a mobile section of DNA (e.g. plasmid, transposon etc) resulting in two or more resistance mechanisms being transferred to a new organism at the same time.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Benzylpenicillin sodium rapidly appears in the blood following intramuscular injection of water-soluble salts and maximum concentrations are usually reached in 15-30 minutes. Peak plasma concentrations of about 12 mcg/ml have been reported after doses of 600 mg with therapeutic plasma concentrations for most susceptible organisms detectable for about 5 hours. Approximately 60% of the dose injected is reversibly bound to plasma protein.
In adults with normal renal function the plasma half-life is about 30 minutes. Most of the dose (60-90%) undergoes renal elimination, 10% by glomerular filtration and 90% by tubular secretion. Tubular secretion is inhibited by probenecid, which is sometimes given to increase plasma penicillin concentrations. Biliary elimination of benzylpenicillin sodium accounts for only a minor fraction of the dose.
Preclinical safety data
There are no pre-clinical data of relevance to the prescriber which are additional to that already included in other sections of the SmPC.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.