BIMZELX Solution for injection Ref.[27933] Active ingredients: Bimekizumab
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2025 Publisher: UCB Pharma S.A., Allée de la Recherche 60, B-1070 Bruxelles, Belgium
5.1. Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Immunosuppressants, interleukin inhibitors
ATC code: L04AC21
Mechanism of action
Bimekizumab is a humanised IgG1/κ monoclonal antibody that selectively binds with high affinity to IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-17AF cytokines, blocking their interaction with the IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor complex. Elevated concentrations of IL-17A and IL-17F have been implicated in the pathogenesis of several immune-mediated inflammatory diseases including plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and hidradenitis suppurativa. IL-17A and IL-17F cooperate and/or synergize with other inflammatory cytokines to induce inflammation. IL17-F is produced in significant amount by innate immune cells. This production can be independent of IL-23. Bimekizumab inhibits the proinflammatory cytokines, resulting in the normalization of skin inflammation and substantial decrease of local and systemic inflammation, and as a consequence improvement in clinical signs and symptoms associated with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and hidradenitis suppurativa. From in vitro models, bimekizumab was shown to inhibit psoriasis-related gene expression, cytokine production, the migration of inflammatory cells and pathological osteogenesis to a greater extent than inhibition of IL-17A alone.
Clinical efficacy and safety
Plaque psoriasis
The safety and efficacy of bimekizumab was evaluated in 1,480 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in three Phase 3 multicentre, randomised, placebo and/or active comparator-controlled studies. Patients were at least 18 years of age, had a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score ≥12 and Body Surface Area (BSA) affected by psoriasis (PSO) ≥10%, an Investigators Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥3 on a 5-point scale and were candidates for systemic psoriasis therapy and/or phototherapy. The efficacy and safety of bimekizumab were evaluated versus placebo and ustekinumab (BE VIVID – PS0009), versus placebo (BE READY – PS0013) and versus adalimumab (BE SURE – PS0008).
The BE VIVID study evaluated 567 patients for 52 weeks where patients were randomised to receive either bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks, ustekinumab (45 mg or 90 mg, depending on patient weight, at baseline and week 4 and then every 12 weeks), or placebo for an initial 16 weeks, followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks.
The BE READY study evaluated 435 patients for 56 weeks. Patients were randomised to receive bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks or placebo. At week 16, patients who achieved a PASI 90 response entered the 40-week randomised withdrawal period. Patients initially randomised to bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks were re-randomised to either bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks or bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks or placebo (i.e. withdrawal of bimekizumab). Patients initially randomised to placebo continued to receive placebo provided they were PASI 90 responders. Patients who did not achieve a PASI 90 response at week 16 entered an open-label escape arm and received bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks for 12 weeks. Patients who relapsed (did not achieve PASI 75 response) during the randomised withdrawal period also entered the 12-week escape arm.
The BE SURE study evaluated 478 patients for 56 weeks. Patients were randomised to receive either bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks through week 56, bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks through week 16 followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks through week 56 or adalimumab as per labeling recommendation through Week 24 followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks through week 56.
Baseline characteristics were consistent across all 3 studies: patients were predominantly male (70.7%) and white (84.1%), with a mean age of 45.2 years (18 to 83 years), and 8.9% were ≥65 years of age. The median baseline BSA was 20%, the median baseline PASI score was 18 and the baseline IGA score was severe in 33% of patients. The median baseline scores for Patient Symptoms Diary (PSD) pain, itch and scaling items ranged between 6 and 7 on a 0-10 points scale and the median baseline Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) total score was 9.
Across all 3 studies, 38% of patients had received a prior biologic therapy; 23% had received at least one anti-IL17 agent (primary anti-IL17 failures were excluded) and 13% had received at least one TNF-antagonist. Twenty-two percent were naïve to any systemic therapy (including non-biologic and biologic) and 39% of patients had received prior phototherapy or photochemotherapy.
The efficacy of bimekizumab was evaluated with respect to impact on skin disease overall, specific body locations (scalp, nails, palms and soles), patient reported symptoms and impact on quality of life. The two co-primary endpoints in all 3 studies were the proportion of patients who achieved 1) a PASI 90 response and 2) an IGA “clear or almost clear” (IGA 0/1with at least two points improvement from baseline) response at week 16. PASI 100, IGA 0 response at week 16 and PASI 75 response at week 4 were secondary endpoints in all 3 studies.
Skin disease overall
Treatment with bimekizumab resulted in significant improvement across efficacy endpoints compared to placebo, ustekinumab or adalimumab at week 16. The main efficacy results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Summary of clinical responses in BE VIVID, BE READY and BE SURE:
| BE VIVID | BE READY | BE SURE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=83) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=321) n (%) | Ustekinumab (N=163) n (%) | Placebo (N=86) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=349) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=319) n (%) | Adalimumab (N=159) n (%) | |
| PASI 100 Week 16 | 0 (0.0) | 188 (58.6)a | 34 (20.9) | 1 (1.2) | 238 (68.2)a | 194 (60.8)a | 38 (23.9) |
| PASI 90 Week 16 | 4 (4.8) | 273 (85.0)a,b | 81 (49.7) | 1 (1.2) | 317 (90.8)a | 275 (86.2)a | 75 (47.2) |
| PASI 75 Week 4 Week 16 | 2 (2.4) 6 (7.2) | 247 (76.9)a,b 296 (92.2) | 25 (15.3) 119 (73.0) | 1 (1.2) 2 (2.3) | 265 (75.9)a 333 (95.4) | 244 (76.5)a 295 (92.5) | 50 (31.4) 110 (69.2) |
| IGA 0 Week 16 | 0 (0.0) | 188 (58.6)a | 36 (22.1) | 1 (1.2) | 243 (69.6)a | 197 (61.8) | 39 (24.5) |
| IGA 0/1 Week 16 | 4 (4.8) | 270 (84.1)a,b | 87 (53.4) | 1 (1.2) | 323 (92.6)a | 272 (85.3)a | 91 (57.2) |
| Absolute PASI ≤2 Week 16 | 3 (3.6) | 273 (85.0) | 84 (51.5) | 1 (1.2) | 315 (90.3) | 280 (87.8) | 86 (54.1) |
| PSD Pain improvement ≥4 (N) Week 16 | (N=48) 5 (10.4) | (N=190) 140 (73.7) | (N=90) 54 (60.0) | (N=49) 0 (0.0) | (N=209) 148 (70.8) | (N=222) 143 (64.4) | (N=92) 43 (46.7) |
| PSD Itch improvement ≥4 (N) Week 16 | (N=53) 6 (11.3) | (N=222) 151 (68.0) | (N=104) 57 (54.8) | (N=60) 0 (0.0) | (N=244) 161 (66.0) | (N=248) 153 (61.7) | (N=107) 42 (39.3) |
| PSD Scaling improvement ≥4 (N) Week 16 | (N=56) 6 (10.7) | (N=225) 171 (76.0) | (N=104) 59 (56.7) | (N=65) 1 (1.5) | (N=262) 198 (75.6) | (N=251) 170 (67.7) | (N=109) 42 (38.5) |
Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W=bimekizumab every 4 weeks. Non-Responder Imputation (NRI) is used.
IGA 0/1 response was defined as Clear (0) or Almost Clear (1) with at least a 2-category improvement from Baseline at week 16. IGA 0 response was defined as Clear (0) with at least a 2-category improvement from Baseline at week 16.
PSD is a Patient Symptoms Diary, also referred to as Psoriasis Symptoms and Impacts Measure (P-SIM), measuring psoriasis symptom severity on a scale from 0 (no symptoms) to 10 (very severe symptoms). Response is defined as a decrease ≥4 from baseline to week 16 for pain, itch and scaling on a scale from 0 to 10.
a p<0.001 versus placebo (BE VIVID and BE READY), versus adalimumab (BE SURE), adjusted for multiplicity.
b p<0.001 versus ustekinumab (BE VIVID), adjusted for multiplicity.
Bimekizumab was associated with a rapid onset of efficacy. In BE VIVID, at week 2 and week 4, PASI 90 response rates were significantly higher for bimekizumab-treated patients (12.1% and 43.6% respectively) compared to placebo (1.2% and 2.4% respectively) and ustekinumab (1.2% and 3.1% respectively).
In the BE VIVID study, at week 52, bimekizumab-treated patients (every 4 weeks) achieved significantly higher response rates than the ustekinumab-treated patients on the endpoints of PASI 90 (81.9% bimekizumab vs 55.8% ustekinumab, p<0.001), IGA 0/1 (78.2% bimekizumab vs 60.7% ustekinumab, p<0.001) and PASI 100 (64.5% bimekizumab vs 38.0% ustekinumab).
Figure 1. PASI 90 responder rates over time in BE VIVID:
BKZ 320 mg Q4W=bimekizumab every 4 weeks; Uste=ustekinumab. NRI is used.
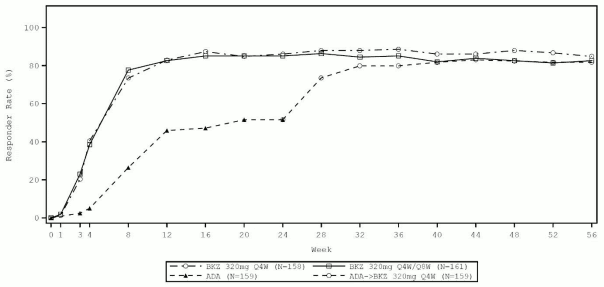
In the BE SURE study at week 24, a significantly higher percentage of patients treated with bimekizumab (Q4W/Q4W and Q4W/Q8W combined dosing arms) achieved PASI 90 and IGA 0/1 responses as compared with adalimumab (85.6% and 86.5% respectively vs 51.6% and 57.9% respectively, p<0.001). At week 56, 70.2% of patients treated with bimekizumab Q8W achieved a PASI 100 response. Among the 65 adalimumab non-responders at week 24 (< PASI 90), 78.5% achieved a PASI 90 response after 16 weeks of treatment with bimekizumab. The safety profile observed in patients who switched from adalimumab to bimekizumab without a wash-out period was similar to patients who initiated bimekizumab after wash out of prior systemic therapies.
Figure 2. PASI 90 responder rates over time in BE SURE:
BKZ 320 mg Q4W = bimekizumab every 4 weeks; BKZ 320 mg Q8W = bimekizumab every 8 weeks; ADA= adalimumab.
Patients in the BKZ Q4W/Q8W group switched from Q4W to Q8W dosing at week 16. Patients in the ADA/BKZ 320 mg Q4W group switched from ADA to BKZ Q4W at week 24. NRI is used.
The efficacy of bimekizumab was demonstrated regardless of age, gender, race, disease duration, body weight, PASI baseline severity and previous treatment with a biologic. Bimekizumab was efficacious in prior biologic exposed patients, including anti-TNF/anti IL-17 and in systemic treatment-naïve patients. Efficacy in patients with primary failure to anti-IL17 has not been investigated.
Based on population PK/PD analysis and supported by clinical data, patients with higher body weight (≥120 kg) who did not achieve complete skin clearance at week 16 benefited from continued bimekizumab 320 mg every four weeks (Q4W) after the initial 16 weeks of treatment. In the BE SURE study, patients received bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W through week 16, followed by either Q4W or every eight weeks (Q8W) dosing through week 56, regardless of responder status at week 16. Patients in the ≥120 kg group (N=37) on the Q4W maintenance regimen showed greater improvement in PASI100 between week 16 (23.5%) and week 56 (70.6%) compared to those on the Q8W maintenance regimen (week 16: 45.0% vs week 56: 60.0%).
Improvements were observed in psoriasis involving the scalp, nails, palms and soles in patients treated with bimekizumab at week 16 (see Table 3).
Table 3. Scalp, palmoplantar and nail responses in BE VIVID, BE READY and BE SURE at week 16:
| BE VIVID | BE READY | BE SURE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W | Ustekinumab | Placebo | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W | Adalimumab | |
| Scalp IGA (N)a Scalp IGA 0/1, n (%) | (72) 11 (15.3) | (285) 240 (84.2)b | (146) 103 (70.5) | (74) 5 (6.8) | (310) 286 (92.3)b | (296) 256 (86.5) | (138) 93 (67.4) |
| pp-IGA (N)a pp-IGA 0/1, n (%) | (29) 7 (24.1) | (105) 85 (81.0) | (47) 39 (83.0) | (31) 10 (32.3) | (97) 91 (93.8) | (90) 75 (83.3) | (34) 24 (70.6) |
| mNAPSI 100 (N)a mNAPSI 100, n (%) | (51) 4 (7.8) | (194) 57 (29.4) | (109) 15 (13.8) | (50) 3 (6.0) | (210) 73 (34.8) | (181) 54 (29.8) | (95) 21 (22.1) |
Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W= bimekizumab every 4 weeks. Non responder imputation (NRI) is used. Scalp IGA 0/1 and pp-IGA 0/1 responses were defined as Clear (0) or Almost Clear (1) with ≥2 category improvement relative to Baseline.
a Include only patients with a scalp Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) of 2 or greater, a palmoplantar IGA of 2 or greater and a modified Nail Psoriasis and Severity Index (mNAPSI) score >0 at baseline.
b p<0.001 versus placebo, adjusted for multiplicity
Scalp IGA and palmoplantar IGA responses in bimekizumab-treated patients were maintained through week 52/56. Nail psoriasis continued to improve beyond week 16. In BE VIVID, at week 52, 60.3% of patients treated with bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks achieved complete nail clearance (mNAPSI 100). In BE READY, at week 56, 67.7% and 69.8% of week 16 PASI 90 responders achieved complete nail clearance with bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks and bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks respectively.
Maintenance of response
Table 4. Maintenance of responses with bimekizumab at week 52 in PASI100, PASI90, IGA 0/1 and Absolute PASI ≤2 responders at week 16*:
| PASI 100 | PASI 90 | IGA 0/1 | Absolute PASI ≤2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320mg Q4W (N=355) n (%) | 320mg Q8W (N=182) n (%) | 320mg Q4W (N=516) n (%) | 320mg Q8W (N=237) n (%) | 320mg Q4W (N=511) n (%) | 320mg Q8W (N=234) n (%) | 320mg Q4W (N=511) n (%) | 320mg Q8W (N=238) n (%) |
| 295 (83.1) | 161 (88.5) | 464 (89.9) | 214 (90.3) | 447 (87.5) | 214 (91.5) | 460 (90.0) | 215 (90.3) |
* Integrated analysis of BE VIVID, BE READY and BE SURE. NRI is used.
320 mg Q4W: bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks from week 16.
320 mg Q8W: bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks from week 16.
Durability of response (after bimekizumab discontinuation)
Figure 3. PASI 90 responder rates over time for PASI 90 responders at week 16 – Randomized withdrawal period in BE READY:
NRI is used.
At week 16, 105 study participants started the Randomized-Withdrawal Period in the bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W/placebo group, 100 in the bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W/Q8W group, and 106 in the bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W/Q4W group.
In BE READY, for PASI 90 responders at week 16 who were re-randomised to placebo and withdrawn from bimekizumab, the median time to relapse, defined as loss of PASI 75, was approximately 28 weeks (32 weeks after the last bimekizumab dose). Among these patients, 88.1% regained a PASI 90 response within 12 weeks of restarting treatment with bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks.
Health-related Quality of Life / Patient reported outcomes
Across all 3 studies, a greater proportion of patients treated with bimekizumab experienced no impact of psoriasis on their quality of life as measured by the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) compared to placebo and active comparator-treated patients at week 16 (Table 5).
Table 5. Quality of life in study BE VIVID, BE READY and BE SURE:
| BE VIVID | BE READY | BE SURE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=83) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=321) n (%) | Ustekinumab (N=163) n (%) | Placebo (N=86) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=349) n (%) | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W (N=319) n (%) | Adalimumab (N=159) n (%) | |
| DLQI 0/1a Baseline | 3 (3.6) | 16 (5.0) | 5 (3.1) | 4 (4.7) | 11 (3.2) | 10 (3.1) | 13 (8.2) |
| DLQI 0/1a Week 16 | 10 (12.0) | 216 (67.3) | 69 (42.3) | 5 (5.8) | 264 (75.6) | 201 (63.0) | 74 (46.5) |
a DLQI absolute score of 0 or 1 indicates no impact of the disease on health-related quality of life. NRI is used.
DLQI 0/1 responses continued to increase beyond week 16 and then were maintained through week 52/56. In BE VIVID, DLQI 0/1 response rate at week 52 was 74.8% in patients treated with bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks. In BE SURE at week 56, 78.9% and 74.1% of patients had a DLQI 0/1 with bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks and bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks, respectively.
Phase 3 Open Label Extension study
Patients who completed one of the pivotal phase 3 studies (‘feeder studies’) could enter a 144-week open-label extension study (PS0014) to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of bimekizumab.
344 patients who were treated with bimekizumab 320 mg every 8 weeks (BKZ 320 mg Q8W) or every 4 weeks (BKZ 320 mg Q4W) during the feeder study, and who achieved PASI 90 at the end of the feeder study, received bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W throughout PS0014. Of these, 293 (85.2%) patients completed 144 weeks of treatment with bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W. 48 patients (14.0%) discontinued the study during the treatment period, of which 21 (6.1%) discontinued due to an adverse event and 4 (1.2%) discontinued due to lack of efficacy.
Among the patients remaining in the study, improvements achieved with bimekizumab for the efficacy endpoints PASI 90 and IGA 0/1 in the feeder studies were maintained through an additional 144 weeks of open-label treatment.
Phase 3b direct comparative study versus secukinumab
The efficacy and safety of bimekizumab were also evaluated in a double-blind study compared with secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor, (BE RADIANT – PS0015). Patients were randomized to receive bimekizumab (N=373, 320mg at Week 0, 4, 8, 12 and 16 (Q4W) followed by 320mg every 4 weeks (Q4W/Q4W) or 320 mg every 8 weeks (Q4W/Q8W)) or secukinumab (N=370, 300 mg at Weeks 0,1, 2, 3, 4 followed by 300 mg every 4 weeks). Baseline characteristics were consistent with a population of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis patients with a median BSA of 19% and a median PASI score of 18.
Bimekizumab-treated patients achieved significantly higher response rates compared to secukinumab for the primary endpoint of PASI100 (complete skin clearance) at Week 16. Significantly higher response rates were also achieved with bimekizumab for the secondary endpoint of PASI 100 at Week 48 (for both Q4W/Q4W and Q4W/Q8W regimens). Comparative PASI response rates are presented in Table 6.
Differences in response rates between bimekizumab and secukinumab-treated patients were noted as early as week 1 for PASI 75 (7.2% and 1.4% respectively) and as early as Week 2 for PASI 90 (7.5% and 2.4% respectively).
Table 6. PASI response rates from BE RADIANT – bimekizumab versus secukinumab:
| Week 4 | Week 16 | Week 48a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W | Secukinumab | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W | Secukinumab | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W/Q4W | Bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W/Q8W | Secukinumab | |
| (N=373) n (%) | (N=370) n (%) | (N=373) n (%) | (N=370) n (%) | (N=147) n (%) | (N=215) n (%) | (N=354) n (%) | |
| PASI 100 | 52 (13.9) | 23 (6.2) | 230 (61.7)* | 181 (48.9) | 108 (73.5)* | 142 (66.0)* | 171 (48.3) |
| PASI 90 | 134 (35.9) | 65 (17.6) | 319 (85.5) | 275 (74.3) | 126 (85.7) | 186 (86.5) | 261 (73.7) |
| PASI 75 | 265 (71.0)* | 175 (47.3) | 348 (93.3) | 337 (91.1) | 134 (91.2) | 196 (91.2) | 301 (85.0) |
| Absolute PASI <2 | 151 (40.5) | 75 (20.3) | 318 (85.3) | 283 (76.5) | 127 (86.4) | 186 (86.5) | 269 (76.0) |
a Data are from the Maintenance Set consisting of patients who received at least one dose of study treatment at Week 16 or later
* p<0.001 versus secukinumab, adjusted for multiplicity. NRI is used.
Bimekizumab and secukinumab PASI 100 response rates through Week 48 are presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4. PASI 100 response rate over time in BE RADIANT:
NRI is used. Maintenance Set consisting of patients who received at least one dose of study treatment at Week 16 or later
The efficacy of bimekizumab in BE RADIANT was consistent with BE VIVID, BE READY and BE SURE.
Phase 3b Open Label Extension period
At week 48, patients were allowed to enter a 96-week open-label extension period (OLE) and started or continued with bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W or 320 mg Q8W depending on their PASI 90 responder status at week 48. Study participants who initially received bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W during the OLE were switched to bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W at week 72 or later.
231 patients who were treated with bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W or bimekizumab 320 mg Q4W and achieved PASI 90 at week 48 received bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W throughout the OLE. Of these patients, 31 (13.4%) discontinued the study during the OLE, of which 10 (4.3%) discontinued due to an adverse event and 1 (0.4%) discontinued due to lack of efficacy.
116 patients who were treated with secukinumab and achieved PASI 90 at week 48 received bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W throughout the OLE. Of these patients, 16 (13.8%) discontinued the study during the OLE, of which 6 (5.2%) discontinued due to an adverse event and 1 (0.9%) discontinued due to lack of efficacy.
Among the patients remaining in the study, improvements achieved with bimekizumab or secukinumab for the efficacy endpoints PASI 100, PASI 90, PASI 75 and PASI ≤2 responder at week 48 were maintained on treatment with bimekizumab 320 mg Q8W through an additional 96 weeks of open-label treatment.
The safety profile of bimekizumab up to week 144 was consistent with the safety profile observed up to 48 weeks.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
The safety and efficacy of bimekizumab were evaluated in 1112 adult patients (at least 18 years of age) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in two multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (PA0010 – BE OPTIMAL and PA0011- BE COMPLETE). The BE OPTIMAL study included an active reference treatment arm (adalimumab) (N=140).
For both studies, patients had a diagnosis of active psoriatic arthritis for at least 6 months based on the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) and had active disease with tender joint count (TJC) ≥3 and swollen joint count (SJC) ≥3. Patients had a diagnosis of PsA for a median of 3.6 years in BE OPTIMAL and 6.8 years in BE COMPLETE. Patients with each subtype of PsA were enrolled in these studies, including polyarticular symmetric arthritis, oligoarticular asymmetric arthritis, distal interphalangeal joint predominant, spondylitis predominant and arthritis mutilans. At baseline, 55.9% of patients had ≥3% Body Surface Area (BSA) with active plaque psoriasis. 10.4% of patients had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and 31.9% and 12.3% had enthesitis and dactylitis at baseline, respectively. The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50 response at Week 16.
The BE OPTIMAL study evaluated 852 patients not previously exposed to any biologic diseasemodifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD) for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis or psoriasis. Patients were randomized (3:2:1) to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks through Week 52 or placebo up to Week 16 followed by bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks through Week 52 or an active reference treatment arm (adalimumab 40mg every 2 weeks) up to Week 52. In this study, 78.3% of patients had received prior treatment with ≥ 1 cDMARDs and 21.7 % of patients had no prior treatment with cDMARDs. At baseline, 58.2% of patients were receiving concomitant methotrexate (MTX), 11.3% were receiving concomitant cDMARDs other than MTX, and 30.5% were receiving no cDMARDs.
The BE COMPLETE study evaluated 400 patients with an inadequate response (lack of efficacy) or intolerance to treatment with 1 or 2 tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (anti-TNFα – IR) for either psoriatic arthritis or psoriasis. Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks or placebo up to Week 16. At baseline, 42.5% of patients were receiving concomitant MTX, 8.0% were receiving concomitant cDMARDs other than MTX, and 49.5% were receiving no cDMARDs. In this study, 76.5% of participants had an inadequate response to 1 TNFα inhibitor, 11.3% had an inadequate response to 2 TNFα inhibitors and 12.3% were intolerant to TNFα inhibitors.
Signs and symptoms
In bDMARDs-naïve patients (BE OPTIMAL) and anti-TNFα IR patients (BE COMPLETE) treatment with bimekizumab resulted in significant improvement in signs and symptoms and measures of disease activity compared to placebo at Week 16, with similar response rates seen in both patient populations (see Table 7). Clinical responses were sustained up to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL as assessed by ACR 20, ACR 50, ACR 70, MDA, PASI 90, PASI 100 and ACR 50/PASI 100.
Table 7. Clinical response in study BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE:
| BE OPTIMAL (bDMARD-naïve) | BE COMPLETE (anti TNFα-IR) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=281) n (%) | BKZ 160mg Q4W (N=431) n (%) | Difference from placebo (95% CI)d | Reference Arme (Adalimumab) (N=140)e n (%) | Placebo (N=133) n (%) | BKZ 160 mg Q4W (N=267) n (%) | Difference from placebo (95% CI)d | |
| ACR 20 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 67 (23.8) - | 268 (62.2) 282 (65.4) 307 (71.2) | 38.3 (31.4, 45.3) | 96 (68.6) 99 (70.7) 102 (72.9) | 21 (15.8) | 179 (67.0) | 51.2 (42.1, 60.4) |
| ACR 50 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 28 (10.0) - | 189 (43.9)* 196 (45.5) 235 (54.5) | 33.9 (27.4, 40.4) | 64 (45.7) 66 (47.1) 70 (50.0) | 9 (6.8) | 116 (43.4)* | 36.7 (27.7, 45.7) |
| ACR 70 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 12 (4.3) - | 105 (24.4) 126 (29.2) 169 (39.2) | 20.1 (14.7, 25.5) | 39 (27.9) 42 (30.0) 53 (37.9) | 1 (0.8) | 71 (26.6) | 25.8 (18.2, 33.5) |
| MDAa Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 37 (13.2) - | 194 (45.0)* 209 (48.5) 237 (55.0) | 31.8 (25.2, 38.5) | 63 (45.0) 67 (47.9) 74 (52.9) | 8 (6.0) | 118 (44.2)* | 38.2 (29.2, 47.2) |
| Patients with ≥3% BSA | (N=140) | (N=217) | (N=68) | (N=88) | (N=176) | ||
| PASI 90 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 4 (2.9) - | 133 (61.3)* 158 (72.8) 155 (71.4) | 58.4 (49.9, 66.9) | 28 (41.2) 32 (47.1) 41 (60.3) | 6 (6.8) | 121 (68.8)* | 61.9 (51.5, 72.4) |
| PASI 100 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 3 (2.1) - | 103 (47.5) 122 (56.2) 132 (60.8) | 45.3 (36.7, 54.0) | 14 (20.6) 26 (38.2) 33 (48.5) | 4 (4.5) | 103 (58.5) | 54.0 (43.1, 64.8) |
| ACR50/PASI 100 Week 16 Week 24 Week 52 | 0 - | 60 (27.6) 68 (31.3) 102 (47.0) | NC (NC, NC) | 11 (16.2) 17 (25.0) 24 (35.3) | 1 (1.1) | 59 (33.5) | 32.4 (22.3, 42.5) |
| Patients with LDI>0b | (N=47) | (N=90) | |||||
| Dactylitis free stateb Week 16 | 24 (51.1) | 68 (75.6)*** | 24.5 (8.4, 40.6) | ||||
| Patients with LEI>0c | (N=106) | (N=249) | |||||
| Enthesitis free statec Week 16 | 37 (34.9) | 124 (49.8)** | 14.9 (3.7, 26.1) | ||||
ACR50/PASI100 = composite ACR50 and PASI100 response. BKZ 160 mg Q4W = bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks. CI = confidence interval. NC = Not calculable
a A patient was classified as achieving Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) when meeting 5 of the 7 following criteria: tender joint count ≤1; swollen joint count ≤1; Psoriasis Activity and Severity Index ⩽1 or body surface area ≤3; patient pain visual analogue scale (VAS) ≤15; patient global disease activity VAS ≤20; Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index ≤0.5; tender entheseal points ≤1
b Based on pooled data from BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE studies for patients with baseline Leeds Dactylitis Index (LDI) >0. Dactylitis free state is LDI=0
c Based on pooled data from BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE studies for patients with baseline Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) >0. Enthesitis free state is LEI =0
d Unadjusted differences are shown
e No statistical comparison to bimekizumab or placebo performed
* p<0.001 versus placebo adjusted for multiplicity. **p=0.008 versus placebo adjusted for multiplicity. ***p=0.002 versus placebo adjusted for multiplicity. NRI is used. Other endpoints at Week 16 and all endpoints at Week 24 and Week 52 were not part of the sequential testing hierarchy and any comparisons are nominal.
Improvements from baseline were shown in all individual ACR components with bimekizumab at Week 16 and were sustained up to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL.
Treatment responses on bimekizumab were significantly greater than those on placebo as early as Week 2 for ACR 20 (BE OPTIMAL, 27.1% versus 7.8%, nominal p<0.001) and Week 4 for ACR 50 (BE OPTIMAL, 17.6% versus 3.2%, nominal p<0.001 and BE COMPLETE, 16.1% versus 1.5%, nominal p<0.001).
Figure 5. ACR 50 response over time up to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL (NRI):
Figure 6. ACR 50 response over time up to Week 16 in BE COMPLETE (NRI):
For the bimekizumab-treated patients who achieved an ACR 50 response at Week 16 in BE OPTIMAL, 87.2% maintained this response at Week 52.
The efficacy and safety of bimekizumab were demonstrated regardless of age, gender, race, baseline body weight, baseline psoriasis involvement, baseline CRP, disease duration and prior cDMARDs use. In both studies, similar responses were observed with bimekizumab regardless of whether patients were on concomitant cDMARDs, including MTX, or not.
The modified Psoriatic Arthritis Response Criteria (PsARC) is a specific composite responder index comprising of tender joint count, swollen joints count, patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients achieving modified PsARC at Week 16 was higher in the bimekizumab-treated patients compared to placebo (80.3% versus 40.2% respectively in BE OPTIMAL and 85.4% versus 30.8% respectively in BE COMPLETE). PsARC response was sustained up to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL.
Radiographic response
In BE OPTIMAL, inhibition of progression of structural damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as the change from baseline in the Van der Heijde modified total Sharp Score (vdHmTSS) and its components, the Erosion Score (ES) and the Joint Space Narrowing score (JSN) at Week 16 (see Table 8).
Table 8. Change in vdHmTSS in BE OPTIMAL at Week 16:
| Placebo | BKZ 160mg Q4W | Difference from placebo (95% CI)a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population with elevated hs-CRP and/or at least 1 bone erosion at baseline | (N=227) | (N=361) | |
| Mean change from baseline (SE) | 0.36 (0.10) | 0.04 (0.05)* | -0.32 ( -0.35, -0.30) |
| Overall population | (N=269) | (N=420) | |
| Mean change from baseline (SE) | 0.32 (0.09) | 0.04 (0.04)* | -0.26 ( -0.29, -0.23) |
* p=0.001 versus placebo. p-values are based on reference-based imputation using difference in LS Mean using an ANCOVA model with treatment, bone erosion at Baseline and region as fixed effects and Baseline score as a covariate.
Week 16 summary data is based on the first set of reads for the primary analysis.
a Unadjusted differences are shown
Bimekizumab significantly inhibited the progression of joint damage at Week 16 in both the population with elevated hs-CRP and/or at least 1 bone erosion at baseline and the overall population compared to placebo. While reference-based imputation was specified as the missing data handling method in the statistical testing procedure comparing bimekizumab versus placebo, changes from baseline were also calculated using standard multiple imputation in both the population with elevated hs-CRP and/or at least 1 bone erosion at baseline and the overall population at Week 16 in the bimekizumab arm (mean change from baseline 0.01 and 0.01 respectively) and the adalimumab arm (mean change from baseline -0.05 and -0.03 respectively). Inhibition of the progression of joint damage was sustained in both the population with elevated hs-CRP and/or at least 1 bone erosion at baseline and the overall population to Week 52 in both the bimekizumab arm (mean change from baseline 0.10 and 0.10 respectively) and the adalimumab arm (mean change from baseline -0.17 and -0.12 respectively).
The observed percentage of patients with no radiographic joint damage progression (defined as a change from baseline in mTSS of ≤0.5) from randomization to Week 52 was 87.9% (N=276/314) for bimekizumab and 84.8% (N=168/198) for placebo study participants switching to bimekizumab and 94.1% (N=96/102) for adalimumab in the population with elevated hs-CRP and/or at least 1 bone erosion. Similar rates were observed in the overall population (89.3% (N=326/365) for bimekizumab and 87.3% (N=207/237) for placebo study participants switching to bimekizumab and 94.1% (N=111/118) for adalimumab).
Physical function and other health-related outcomes
Both bDMARD-naïve (BE OPTIMAL) and anti-TNFα-IR (BE COMPLETE) patients receiving bimekizumab showed significant improvement from baseline in physical function compared to placebo patients at Week 16 (p<0.001) as assessed by the HAQ-DI (LS Mean change from baseline: -0.3 versus -0.1 in BE OPTIMAL and – 0.3 versus 0 in BE COMPLETE, respectively). In both studies, a greater proportion of patients achieved a clinically meaningful reduction of at least 0.35 in HAQ-DI score from baseline in the bimekizumab group compared with placebo at Week 16.
Bimekizumab-treated patients reported significant improvement from baseline in the Short Form-36 item Health Survey Physical Component Summary (SF-36 PCS) score at Week 16 compared to placebo (LS Mean change from baseline: 6.3 versus 1.9, p<0.001 in BE OPTIMAL and 6.2 versus 0.1, p<0.001 in BE COMPLETE).
In both studies, bimekizumab-treated patients reported meaningful reduction from baseline in fatigue as measured by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue score at Week 16 compared to placebo. Meaningful improvement from baseline was also observed in the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease-12 (PsAID-12) score in the bimekizumab-treated group compared to the placebo group at Week 16.
Patients with axial involvement at baseline, approximately 74% of patients, (defined as a Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score ≥4) showed greater improvement from baseline in BASDAI compared with placebo at Week 16.
Improvements achieved at Week 16 in all measures of physical function and other health-related outcomes mentioned above (HAQ-DI, SF-36 PCS, FACIT-Fatigue, PsAID-12 scores and BASDAI) were sustained up to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL.
In BE OPTIMAL, at Week 52, 65.5% of patients treated with bimekizumab achieved complete nail clearance (mNAPSI resolution in patients with mNAPSI higher than 0 at Baseline).
Axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA and AS)
The efficacy and safety of bimekizumab was evaluated in 586 adult patients (at least 18 years of age) with active axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled studies, one in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) and one in ankylosing spondylitis (AS), also known as radiographic axSpA. The primary endpoint in both studies was the percentage of patients achieving an Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) 40 response at Week 16. Consistent results were seen across both patient populations.
The BE MOBILE 1 study (AS0010) evaluated 254 patients with active nr-axSpA. Patients had axSpA (age of symptoms onset <45 years) meeting the ASAS classification criteria and had active disease as defined by a Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥4 and spinal pain ≥4 on a 0 to 10 numeric rating scale (NRS) (from BASDAI Item 2) and no evidence of radiographic changes in the sacroiliac joints that would meet the modified New York criteria for AS. Patients also had objective signs of inflammation as indicated by elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) level and/or evidence of sacroiliitis on Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) as well as a history of inadequate response to 2 different non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or intolerance or contraindication to NSAIDs. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks up to Week 52 or placebo up to Week 16 followed by bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks up to Week 52. At baseline, patients had symptoms of nr-axSpA for a mean of 9 years (median of 5.5 years). 10.6% of patients were previously treated with an anti-TNFα agent.
The BE MOBILE 2 study (AS0011) evaluated 332 patients with active AS determined by documented radiologic evidence (x-ray) fulfilling the Modified New York criteria for AS. Patients had active disease as defined by a BASDAI ≥4 and spinal pain ≥4 on a 0 to 10 numeric rating scale (NRS) (from BASDAI Item 2). Patients had to have a history of inadequate response to 2 different NSAIDs or intolerance or contraindication to NSAIDs. Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks up to Week 52 or placebo up to Week 16 followed by bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks up to Week 52. At baseline, patients had symptoms of AS for a mean of 13.5 years (median of 11 years). 16.3% of patients were previously treated with an anti-TNFα agent.
Clinical response
Treatment with bimekizumab resulted in significant improvement in signs and symptoms and measures of disease activity compared to placebo at Week 16 in both nr-axSpA and AS patient populations (see Table 9). Clinical responses were sustained up to Week 52 in both patient populations as assessed by all the endpoints presented in Table 9.
Table 9. Clinical responses in BE MOBILE 1 and BE MOBILE 2:
| BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA) | BE MOBILE 2 (AS) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=126) n (%) | BKZ 160 mg Q4W (N=128) n (%) | Difference from placebo (95% CI)a | Placebo (N=111) n (%) | BKZ 160 mg Q4W (N=221) n (%) | Difference from placebo (95% CI)a | |
| ASAS 40 | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | 27 (21.4) | 61 (47.7)* 78 (60.9) | 26.2 (14.9, 37.5) | 25 (22.5) | 99 (44.8)* 129 (58.4) | 22.3 (11.5, 33.0) |
| ASAS 40 in anti-TNFα naives | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | (N=109) 25 (22.9) | (N=118) 55 (46.6) 73 (61.9) | 24.8 (12.4, 37.1) | (N=94) 22 (23.4) | (N=184) 84 (45.7)* 108 (58.7) | 22.3 (10.5, 34.0) |
| ASAS 20 | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | 48 (38.1) | 88 (68.8)* 94 (73.4) | 30.7 (19.0, 42.3) | 48 (43.2) | 146 (66.1)* 158 (71.5) | 22.8 (11.8, 33.8) |
| ASAS-partial remission | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | 9 (7.1) | 33 (25.8)* 38 (29.7) | 18.6 (9.7, 27.6) | 8 (7.2) | 53 (24.0)* 66 (29.9) | 16.8 (8.1, 25.5) |
| ASDAS-major improvement | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | 9 (7.1) | 35 (27.3)* 47 (36.7) | 20.2 (11.2, 29.3) | 6 (5.4) | 57 (25.8)* 71 (32.1) | 20.4 (11.7, 29.1) |
| BASDAI-50 | ||||||
| Week 16 Week 52 | 27 (21.4) | 60 (46.9) 69 (53.9) | 25.3 (14.0, 36.6) | 29 (26.1) | 103 (46.6) 119 (53.8) | 20.5 (9.6, 31.4) |
BKZ 160 mg Q4W = bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks. ASDAS = Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score.
NRI is used.
a Unadjusted differences are shown.
* p<0.001 versus placebo, adjusted for multiplicity.
The proportion of patients in BE MOBILE 1 reaching ASDAS <2.1 (combining ASDAS-inactive disease (ID) and ASDAS-low disease (LD)) at Week 16 was 46.1% in the bimekizumab group versus 21.1% in the placebo group (multiple imputation). At Week 52, 61.6% of patients in the bimekizumab group achieved an ASDAS <2.1, including 25.2% in inactive disease state (ASDAS <1.3).
The proportion of patients in BE MOBILE 2 reaching ASDAS <2.1 (combining ASDAS-ID and ASDAS-LD) at Week 16 was 44.8% in the bimekizumab group versus 17.4% in placebo group (multiple imputation). At Week 52, 57.1% of patients in the bimekizumab group achieved an ASDAS <2.1, including 23.4% in inactive disease state (ASDAS <1.3).
All four ASAS 40 components (total spinal pain, morning stiffness, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index [BASFI] and Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity [PGADA]) were improved with bimekizumab treatment and contributed to the overall ASAS 40 response at week 16, and these improvements were sustained up to Week 52 in both patient populations.
Improvements in other measures of efficacy are shown in Table 10.
Table 10. Other measures of efficacy in BE MOBILE 1 and BE MOBILE 2:
| BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA) | BE MOBILE 2 (AS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=126) | BKZ 160 mg Q4W (N=128) | Placebo (N=111) | BKZ 160 mg Q4W (N=221) | |
| Nocturnal spinal pain | ||||
| Baseline Mean change from baseline at Week 16 Mean change from baseline at Week 52 | 6.7 -1.7 | 6.9 -3.6* -4.3 | 6.8 -1.9 | 6.6 -3.3* -4.1 |
| BASDAI | ||||
| Baseline Mean change from baseline at Week 16 Mean change from baseline at Week 52 | 6.7 -1.5 | 6.9 -3.1* -3.9 | 6.5 -1.9 | 6.5 -2.9* -3.6 |
| BASMI | ||||
| Baseline Mean change from baseline at Week 16 Mean change from baseline at Week 52 | 3.0 -0.1 | 2.9 -0.4 -0.6 | 3.8 -0.2 | 3.9 -0.5** -0.7 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | ||||
| Baseline (Geometric Mean) Ratio to baseline at Week 16 Ratio to baseline at Week 52 | 5.0 0.8 | 4.6 0.4 0.4 | 6.7 0.9 | 6.5 0.4 0.3 |
BASMI = Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index. Hs-CRP = high sensitivity C-reactive protein
MI is used.
* p<0.001 reference-based imputation, versus placebo, adjusted for multiplicity. **p<0.01 reference-based imputation, versus placebo, adjusted for multiplicity
Bimekizumab was associated with a rapid onset of efficacy in both nr-axSpA and AS patient population.
Treatment responses on bimekizumab-treated patients for ASAS 40 were greater than those on placebo as early as Week 1 in BE MOBILE 1 (16.4% vs. 1.6%, nominal p<0.001) and Week 2 in BE MOBILE 2 (16.7% vs. 7.2%, nominal p=0.019).
Bimekizumab was also associated with a rapid decrease in systemic inflammation as measured by hsCRP levels as early as Week 2 in both nr-axSpA and AS patient populations, with nominal p-values <0.001 in both studies.
Figure 7. ASAS 40 response over time up to Week 52 in BE MOBILE 1 (NRI):
Patients on placebo switched to bimekizumab 160 mg Q4W at Week 16
Figure 8. ASAS 40 response over time up to Week 52 in BE MOBILE 2 (NRI):
Patients on placebo switched to Bimekizumab 160 mg Q4W at Week 16
In an integrated analysis of BE MOBILE 1 and BE MOBILE 2, of bimekizumab-treated patients who achieved an ASAS 40 response at Week 16, 82.1% maintained this response at Week 52.
The efficacy of bimekizumab was demonstrated regardless of age, gender, race, disease duration, baseline inflammation status, baseline ASDAS and concomitant cDMARDs. Similar response in ASAS 40 was seen in patients regardless of prior anti-TNFα exposure.
At Week 16, among patients with enthesitis at baseline, the proportion of patients (NRI) with enthesitis resolution as assessed by the Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis (MASES) index was greater with bimekizumab compared to placebo (BE MOBILE 1: 51.1% versus 23.9% and BE MOBILE 2: 51.5% versus 32.8%). The resolution of enthesitis with bimekizumab was sustained up to Week 52 in both studies (BE MOBILE 1: 54.3% and BE MOBILE 2: 50.8%).
Reduction of inflammation
Bimekizumab reduced inflammation as measured by hs-CRP (see Table 10) and as assessed by MRI in an imaging sub-study. Signs of inflammation were assessed by MRI at baseline and Week 16 and expressed as change from baseline in Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) score for sacroiliac joints and Ankylosing Spondylitis spine Magnetic Resonance Imagine-activity (ASspiMRI-a score in the Berlin modification) for the spine. Reduction of inflammatory signs in both sacroiliac joints and the spine was observed in patients treated with bimekizumab as compared with placebo (see Table 11). Reduction of inflammation as measured by hs-CRP and as assessed by MRI was sustained to Week 52.
Table 11. Reduction of inflammation as assessed by MRI in BE MOBILE 1 and BE MOBILE 2:
| BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA) | BE MOBILE 2 (AS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | BKZ 160 mg Q4W | Placebo | BKZ 160 mg Q4W | |
| SPARCC score | ||||
| Mean change from baselinea at week 16 Mean change from baselinea at week 52 | -1.56 (N=62) | -6.15 (N=78) -7.57 (N=67) | 0.59 (N=46) | -4.51 (N=81) -4.67 (N=78) |
| ASspiMRI-a (Berlin modifications) score | ||||
| Mean change from baseline a) at week 16 Mean change from baseline a) at week 52 | 0.03 (N=60) | -0.36 (N=74) -0.70 (N=65) | -0.34 (N=46) | -2.23 (N=81) -2.38 (N=77) |
a Change from baseline values are based on observed cases as assessed by central read of Week 52 dataset.
Physical function and other health-related outcomes
Patients treated with bimekizumab showed significant improvement from baseline in physical function as assessed by the BASFI compared to placebo (LS Mean change from baseline at Week 16 in BE MOBILE 1: -2.4 versus -0.9, p<0.001 and in BE MOBILE 2: -2.0 versus -1.0, p<0.001). Patients treated with bimekizumab reported significant improvement from baseline compared to placebotreated patients in SF-36 PCS score (LS Mean change from baseline at Week 16 in BE MOBILE 1: 9.3 versus 5.4, p<0.001 and in BE MOBILE 2: 8.5 versus 5.2, p<0.001).
Patients treated with bimekizumab reported significant improvement from baseline in health-related quality of life as measured by the AS Quality of Life Questionnaire (ASQoL) compared to placebo (LS Mean change from baseline at Week 16 in BE MOBILE 1: -4.9 versus -2.3, p<0.001 and in BE MOBILE 2: -4.6 versus -3.0, p<0.001) as well as meaningful reduction in fatigue as assessed by the FACIT-Fatigue score (Mean change from baseline at Week 16 in BE MOBILE 1: 8.5 for bimekizumab versus 3.9 for placebo and in BE MOBILE 2: 8.4 for bimekizumab versus 5.0 for placebo).
Improvements achieved at Week 16 in all measures of physical function and other health-related outcomes mentioned above (BASFI, SF-36 PCS, ASQoL and FACIT-Fatigue scores) were sustained up to Week 52 in both studies.
Extra-articular manifestation
In pooled data from BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA) and BE MOBILE 2 (AS), at Week 16, the proportion of patients developing a uveitis event was lower with bimekizumab (0.6%) compared to placebo (4.6%). The incidence of uveitis remained low with long-term treatment with bimekizumab (1.2/100 patient-years in the pooled phase ⅔ studies).
Hidradenitis suppurativa
The safety and efficacy of bimekizumab was evaluated in 1014 adult patients (at least 18 years of age) with moderate to severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) in two Phase 3 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (HS0003 – BE HEARD I and HS0004 – BE HEARD II). Patients had a diagnosis of HS for at least 6 months with Hurley Stage II or Hurley Stage III disease, and with ≥5 inflammatory lesions (i.e. number of abscesses plus number of inflammatory nodules) and had a history of inadequate response to a course of systemic antibiotics for the treatment of HS.
In both studies patients were randomized (2:2:2:1) to receive bimekizumab 320 mg every 2 weeks for 48 weeks (320 mg Q2W/Q2W) or bimekizumab 320 mg every 4 weeks for 48 weeks (320 mg Q4W/Q4W) or bimekizumab 320 mg every 2 weeks to Week 16 followed by 320 mg every 4 weeks up to Week 48 (320 mg Q2W/Q4W) or placebo to Week 16 followed by bimekizumab 320 mg every 2 weeks up to Week 48. Concomitant oral antibiotic use was allowed if the patient was on a stable dose regimen of doxycycline, minocycline, or an equivalent systemic tetracycline for 28 days prior to baseline.
The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response 50 (HiSCR50) at Week 16, i.e. at least a 50% reduction in the total abscess and inflammatory nodule count with no increase in abscess or draining tunnel count relative to baseline.
Baseline characteristics were consistent across both studies and reflective of a population with moderate to severe HS. Patients had a median disease duration of 5.3 years (mean 8.0 years). The proportions of Hurley Stage II and Stage III patients were 55.7% (50.3% in HS0003 and 61.1% in HS0004) and 44.3% (49.7% in HS0003 and 38.9% in HS0004) respectively, and 8.5% were receiving concomitant antibiotic therapy for HS. The mean baseline Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) total score was 11.4. 56.8% of patients were female and the mean age of all patients was 36.6 years. 79.7% of patients were White, and 10.8% were Black or African American. 45.6% of patients were current smokers.
Clinical response
Treatment with bimekizumab resulted in clinically relevant improvement in disease activity compared to placebo at Week 16. Key efficacy results are shown in Table 12 and 13. The results in Table 12 reflect the predefined primary analysis in which any systemic antibiotic use prior to Week 16 resulted in imputation of nonresponse. In Table 13, only systemic antibiotic use considered by the Investigator to be rescue treatment for HS resulted in imputation of nonresponse.
Table 12. Response in BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II at Week 16 – primary analysisa:
| BE HEARD I | BE HEARD II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=72) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=289) | Placebo (N=74) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=291) | |
| HiSCR50, % (95% CI) | 28.7 (18.1, 39.3) | 45.3 (36.8, 53.8) | 47.8* (41.8, 53.7) | 32.2 (21.4, 42.9) | 53.8* (45.4, 62.1) | 52.0* (46.1, 57.8) |
| HiSCR75, % (95% CI) | 18.4 (9.3, 27.5) | 24.7 (17.3, 32.1) | 33.4* (27.8, 39.1) | 15.6 (7.2, 24.0) | 33.7* (25.7, 41.7) | 35.7* (30.1, 41.3) |
| HSSDD worst skin pain responseb (95 CI) | 15.0 (3.6, 26.5) | 22.1 (12.7, 31.4) | 32.3 (25.1, 39.5) | 10.9 (1.7, 20.1) | 28.6 (19.5, 37.8) | 31.8 (25.1, 38.4) |
a Patients who take systemic antibiotics for any reason or who discontinue due to adverse event or lack of efficacy are treated as non-responders at all subsequent visits for responder variables (or are subject to multiple imputation for continuous variables). Other missing data were imputed via multiple imputation.
b Skin pain response, based on the threshold for within-patient clinically meaningful change (defined as at least a 3-point decrease from Baseline in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) weekly worst skin pain score) at Week 16 among study participants with a score of ≥3 at Baseline. For BE HEARD I: N=46 for placebo, N=103 for BKZ Q4W and N=190 for BKZ Q2W; BE HEARD II: N=49 for placebo, N=108 for BKZ Q4W and N=209 for BKZ Q2W.
* p<0.025 versus placebo, adjusted for multiplicity.
Table 13. Response in BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II at Week 16 – supportive analysisa:
| BE HEARD I | BE HEARD II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=72) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=289) | Placebo (N=74) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=291) | |
| HiSCR50, % (95% CI) | 34.0 (23.0, 45.1) | 53.5 (45.0, 62.0) | 55.2 (49.2, 61.1) | 32.3 (21.5, 43.1) | 58.5 (50.2, 66.8) | 58.7 (53.0, 64.5) |
| HiSCR75, % (95% CI) | 18.3 (9.3, 27.3) | 31.4 (23.5, 39.4) | 38.7 (32.9, 44.5) | 15.7 (7.2, 24.1) | 36.4 (28.3, 44.5) | 39.7 (34.0, 45.5) |
| HSSDD worst skin pain responseb (95 CI) | 16.1 (4.5, 27.8) | 25.3 (16.0, 34.7) | 36.7 (29.4, 44.1) | 11.1 (1.8, 20.4) | 32.9 (23.5, 42.4) | 36.7 (29.8, 43.6) |
a Post-hoc analysis (modified nonresponder imputation [mNRI]): Patients who take systemic antibiotics as rescue medication for HS as defined by the Investigator or who discontinue due to adverse event or lack of efficacy are treated as nonresponders at all subsequent visits for responder variables (or are subject to multiple imputation for continuous variables). Other missing data were imputed via multiple imputation.
b Skin pain response, based on the threshold for within-patient clinically meaningful change (defined as at least a 3-point decrease from Baseline in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) weekly worst skin pain score) at Week 16 among study participants with a score of ≥3 at Baseline. For BE HEARD I: N=46 for placebo, N=103 for BKZ Q4W and N=190 for BKZ Q2W; BE HEARD II: N=49 for placebo, N=108 for BKZ Q4W and N=209 for BKZ Q2W.
In both studies, the onset of action of bimekizumab occurred as early as week 2.
The efficacy of bimekizumab was demonstrated regardless of prior biologics therapy and systemic antibiotic use at baseline.
Clinical responses were sustained through Week 48 in both studies (see Table 14).
Table 14. Response in BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II at Week 48 (mNRI*):
| BE HEARD I | BE HEARD II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKZ 320mg Q4W/Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W/Q4W (N=146) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W/Q2W (N=143) | BKZ 320mg Q4W/Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W/Q4W (N=146) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W/Q2W (N=145) | |
| HiSCR50, % | 52.7 | 61.4 | 60.6 | 63.2 | 63.8 | 60.6 |
| HiSCR75, % | 40.5 | 44.7 | 47.6 | 53.9 | 48.8 | 47.3 |
* mNRI (modified non-responder imputation): Patients who take systemic antibiotics as rescue medication for HS as defined by the Investigator or who discontinue due to adverse event or lack of efficacy are treated as non-responders at all subsequent visits for responder variables (or are subject to multiple imputation for continuous variables). Other missing data were imputed via multiple imputation. This exploratory approach to handling missing data was performed post-hoc.
Health-related quality of life
Across both studies, patients treated with bimekizumab experienced greater meaningful improvement compared to placebo in their health-related quality of life as measured by the standard skin-specific DLQI (Table 15).
Table 15. Health-related quality of life in BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II at Week 16:
| BE HEARD I | BE HEARD II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=72) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=289) | Placebo (N=74) | BKZ 320 mg Q4W (N=144) | BKZ 320 mg Q2W (N=291) | |
| DLQI total score | ||||||
| Mean cfba (SE) | -2.9 (0.8) | -5.4 (0.6) | -5.0 (0.4) | -3.2 (0.6) | -4.5 (0.5) | -4.6 (0.3) |
Improvement achieved at Week 16 in health-related quality of life measurements with bimekizumab were sustained through Week 48.
Paediatric population
The European Medicines Agency has deferred the obligation to submit the results of studies with Bimzelx in one or more subsets of the paediatric population in psoriasis, chronic idiopathic arthritis and hidradenitis suppurativa (see section 4.2 for information on paediatric use).
5.2. Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of bimekizumab were similar in patients with plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA and AS).
Based on population PK analyses and using a reference bodyweight of 90 kg, the bimekizumab apparent clearance and volume of distribution, respectively, in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa were estimated to be approximately 31 and 18% higher than for the aforementioned indications, with an estimated half-life in HS of 20 days. Consequently, the median steady state trough concentration at a dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks was approximately 40% lower in HS compared to other indications.
Absorption
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, following a single subcutaneous dose of 320 mg in plaque psoriasis patients, bimekizumab reached a median (2.5th and 97.5th percentile) peak plasma concentration of 25 (12-50) μg/mL, between 3 and 4 days post dose.
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that bimekizumab was absorbed with an average absolute bioavailability of 70.1% in healthy volunteers.
Based on simulated data, the median (2.5th and 97.5th percentile) peak and trough concentration at steady-state following subcutaneous administration of 320 mg every 4 weeks are 43 (20-91) µg/mL and 20 (7-50) µg/mL respectively and steady-state is reached after approximately 16 weeks with every 4 weeks dosing regimen. Compared with exposure after a single dose, the population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that patients exhibited a 1.74-fold increase in peak plasma concentrations and area under the curve (AUC) following repeated four weekly dosing.
After switching from the 320 mg every 4 weeks dosing regimen to 320 mg every 8 weeks dosing regimen at week 16, steady-state is achieved approximately 16 weeks after the switch. Median (2.5th and 97.5th percentile) peak and trough plasma concentrations are 30 (14-60) μg/mL and 5 (1-16) μg/mL respectively.
Distribution
Based on population pharmacokinetic analyses, the median (coefficient of variation ) volume of distribution (V/F) at steady state was 11.2 (30.5) L in plaque psoriasis patients.
Biotransformation
Bimekizumab is a monoclonal antibody and is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous immunoglobulins.
Elimination
Based on population pharmacokinetic analyses, the median (coefficient of variation ) apparent clearance (CL/F) of bimekizumab was 0.337 L/day (32.7) and the mean terminal elimination halflife of bimekizumab was 23 days in clinical studies in patients with plaque psoriasis.
Linearity/non-linearity
Bimekizumab exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics in patients with plaque psoriasis over a dose range from 64 mg to 480 mg following multiple subcutaneous administrations, with apparent clearance (CL/F) being independent of dose.
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic relationship
A population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model was developed using all available data in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis patients. The analysis showed that higher bimekizumab concentrations are related to better Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) and Investigators Global Assessment (IGA) response. A dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks was shown to be an appropriate dose for the initial treatment period and 320 mg every 8 weeks thereafter is appropriate for the maintenance period for the majority of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis patients (see Special Populations, Body weight).
Special populations
Body weight
Population pharmacokinetic modelling indicated that exposure decreased as body weight increased. The average plasma concentration in adult patients weighing ≥120 kg following a 320 mg subcutaneous injection was predicted to be at least 30% lower than in adult patients weighing 90 kg. Dose adjustment may be appropriate in some patients (see section 4.2).
Elderly
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis with a limited number of elderly patients (n=355 for age ≥65 years and n= 47 for age ≥75 years), apparent clearance (CL/F) in elderly patients and patients less than 65 years of age was similar. No dose adjustment is required (see section 4.2).
Renal impairment or hepatic impairment
No specific studies have been conducted to determine the effect of renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of bimekizumab. The renal elimination of intact bimekizumab, an IgG monoclonal antibody, is expected to be low and of minor importance. Similarly, IgGs are mainly eliminated via intracellular catabolism and hepatic impairment is not expected to influence clearance of bimekizumab. Based on population pharmacokinetic analyses, hepatic function markers (ALT/bilirubin) did not have any impact on bimekizumab clearance in patients with plaque psoriasis.
Race
No clinically meaningful differences in bimekizumab exposure were observed in Japanese or Chinese subjects compared to Caucasian subjects in a clinical pharmacokinetic study. No dose adjustment is required.
Gender
Population pharmacokinetic modelling indicated females may have 10% faster apparent clearance (CL/F) compared to males and it is not clinically meaningful. No dose adjustment is required.
5.3. Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on tissue cross-reactivity testing, repeat-dose toxicity studies (including safety pharmacology endpoints and assessment of fertility-related endpoints) and evaluation of pre- and postnatal development in the cynomolgus monkey.
In cynomolgus monkeys, bimekizumab-related effects were limited to mucocutaneous changes consistent with pharmacologic modulation of commensal microflora.
No mutagenicity or carcinogenicity studies were conducted with bimekizumab. However monoclonal antibodies are not expected to damage DNA or chromosomes. In a 26-week chronic toxicology study in cynomolgus monkeys there were no pre-neoplastic or neoplastic lesions observed at a dose resulting in 109 times the human exposure at 320 mg every 4 weeks.
In a peri- and postnatal development study in the cynomolgus monkey, bimekizumab showed no effects on gestation, parturition, infant survival, foetal and postnatal development when administered throughout organogenesis until parturition at a dose resulting in 27 times the human exposure at 320 mg every 4 weeks based on AUC. At birth, serum bimekizumab concentrations in infant monkeys were comparable to those of mothers.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.