EBIXA Oral solution Ref.[28268] Active ingredients: Memantine
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2022 Publisher: H. Lundbeck A/S, Ottiliavej 9, 2500 Valby, Denmark
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated and supervised by a physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's dementia.
Posology
Therapy should only be started if a caregiver is available who will regularly monitor the intake of the medicinal product by the patient. Diagnosis should be made according to current guidelines. The tolerance and dosing of memantine should be reassessed on a regular basis, preferably within three months after start of treatment. Thereafter, the clinical benefit of memantine and the patient's tolerance of treatment should be reassessed on a regular basis according to current clinical guidelines. Maintenance treatment can be continued for as long as a therapeutic benefit is favourable and the patient tolerates treatment with memantine. Discontinuation of memantine should be considered when evidence of a therapeutic effect is no longer present or if the patient does not tolerate treatment.
Adults
Dose titration
The maximum daily dose is 20 mg once daily. In order to reduce the risk of undesirable effects, the maintenance dose is achieved by upward titration of 5 mg per week over the first 3 weeks as follows:
Week 1 (day 1-7): The patient should take 0.5 ml solution (5 mg) equivalent to one pump actuation per day for 7 days.
Week 2 (day 8-14): The patient should take 1 ml solution (10 mg) equivalent to two pump actuations per day for 7 days.
Week 3 (day 15-21): The patient should take 1.5 ml solution (15 mg) equivalent to three pump actuations per day for 7 days.
From Week 4 on: The patient should take 2 ml solution (20 mg) equivalent to four pump actuations once a day.
Maintenance dose
The recommended maintenance dose is 20 mg per day.
Elderly
On the basis of the clinical studies, the recommended dose for patients over the age of 65 years is 20 mg per day (2 ml solution, equivalent to four pump actuations) as described above.
Renal impairment
In patients with mildly impaired renal function (creatinine clearance 50-80 ml/min) no dose adjustment is required. In patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30-49 ml/min) daily dose should be 10 mg (1 ml solution, equivalent to two pump actuations). If tolerated well after at least 7 days of treatment, the dose could be increased up to 20 mg/day according to standard titration scheme. In patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 5-29 ml/min) daily dose should be 10 mg (1 ml solution, equivalent to two pump actuations) per day.
Hepatic impairment
In patients with mild or moderate hepatic impaired function (Child-Pugh A and Child-Pugh B), no dose adjustment is needed. No data on the use of memantine in patients with severe hepatic impairment are available. Administration of Ebixa is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Paediatric population
No data are available.
Method of administration
Ebixa should be taken orally once daily at the same time each day. The solution can be taken with or without food. The solution must not be poured or pumped into the mouth directly from the bottle or the pump, but should be dosed onto a spoon or into a glass of water using the pump.
For detailed instructions on the preparation and handling of the product see section 6.6.
4.9. Overdose
Only limited experience with overdose is available from clinical studies and post-marketing experience.
Symptoms
Relative large overdoses (200 mg and 105 mg/day for 3 days, respectively) have been associated with either only symptoms of tiredness, weakness and/or diarrhoea or no symptoms. In the overdose cases below 140 mg or unknown dose the patients revealed symptoms from central nervous system (confusion, drowsiness, somnolence, vertigo, agitation, aggression, hallucination and gait disturbance) and/or of gastrointestinal origin (vomiting and diarrhoea).
In the most extreme case of overdose, the patient survived the oral intake of a total of 2000 mg memantine with effects on the central nervous system (coma for 10 days, and later diplopia and agitation). The patient received symptomatic treatment and plasmapheresis. The patient recovered without permanent sequelae.
In another case of a large overdose, the patient also survived and recovered. The patient had received 400 mg memantine orally. The patient experienced central nervous system symptoms such as restlessness, psychosis, visual hallucinations, proconvulsiveness, somnolence, stupor, and unconsciousness.
Treatment
In the event of overdose, treatment should be symptomatic. No specific antidote for intoxication or overdose is available. Standard clinical procedures to remove active substance material, e.g. gastric lavage, carbo medicinalis (interruption of potential entero-hepatic recirculation), acidification of urine, forced diuresis should be used as appropriate.
In case of signs and symptoms of general central nervous system (CNS) overstimulation, careful symptomatic clinical treatment should be considered.
6.3. Shelf life
4 years.
Once opened, the contents of the bottle should be used within 3 months.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Do not store above 30°C.
The bottle with the mounted pump may only be kept and transported in a vertical position.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
50 ml (and 10 x 50 ml) in brown glass bottles (Hydrolytic Class II) and 100 ml in brown glass bottles (Hydrolytic Class III).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
No special requirements.
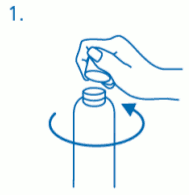
Prior to first use the dosing pump has to be screwed on the bottle. For removing the screw cap from the bottle the cap must be turned anticlockwise and unscrewed completely (fig.1).
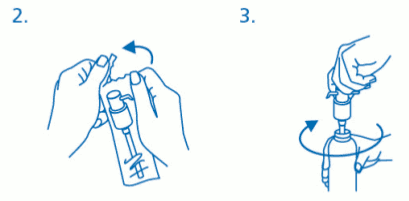
Mounting the dosing pump on the bottle:
The dosing pump has to be removed from the plastic bag (fig. 2) and placed on top of the bottle, sliding the plastic dip tube carefully into the bottle. Then the dosing pump needs to be held onto the neck of the bottle and screwed clockwise until it is firmly attached (fig 3). For the intended use the dosing pump is only screwed on once when starting the use, and should never be unscrewed.
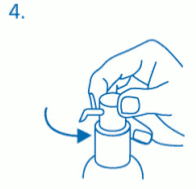
Use of the dosing pump for dispensing:
The dosing pump head has two positions and is easy to turn – anticlockwise (unlocked position) and clockwise (locked position). The dosing pump head should not be pushed down while in the locked position. The solution may only be dispensed in the unlocked position. To do this, the dosing pump head has to be turned in the direction of the arrow about one eighth of a turn, until a resistance is felt (fig. 4)
The dosing pump is then ready for use.
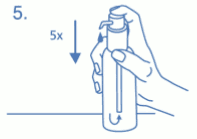
Preparing the dosing pump:
When used for the first time, the dosing pump does not dispense the correct amount of oral solution. Therefore, the pump must be prepared (primed) by pushing the dosing pump head down completely five times in succession (fig. 5).
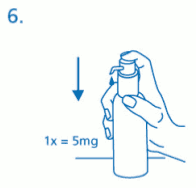
The solution thus dispensed is discarded. The next time the dosing pump head is pushed downwards completely (equivalent to one pump actuation), it dispenses the correct dose (1 pump actuation is equivalent to 0.5 ml oral solution, and contains 5 mg of the active substance memantine hydrochloride; fig. 6).
Correct use of the dosing pump:
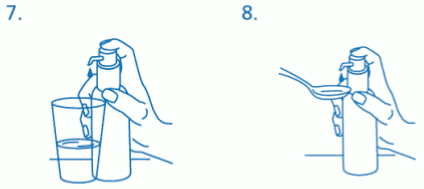
The bottle should be placed on a flat, horizontal surface, for example a table top, and only use it in a vertical position. A glass with a little water or a spoon should be held below the nozzle and the dosing pump head has to be pushed down in a firm but calm and steady manner (not too slowly) right down to the stop (fig. 7, fig. 8).
The dosing pump head can then be released and is ready for the next pump actuation.
The dosing pump may only be used with the memantine hydrochloride solution in the bottle provided, not for other substances or containers. If the pump does not function as described during intended use and according to instruction, the patient should consult the treating physician or a pharmacist. The dosing pump should be locked after use.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.