HUMALOG 100 units/ml Solution for injection in vial / Cartridge / KwikPen - Junior KwikPen Ref.[8011] Active ingredients: Insulin lispro
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2018 Publisher: Eli Lilly Nederland B.V., Papendorpseweg 83, 3528 BJ, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Drugs used in diabetes, insulins and analogues for injection, fast-acting
ATC code: A10AB04
The primary activity of insulin lispro is the regulation of glucose metabolism.
In addition, insulins have several anabolic and anti-catabolic actions on a variety of different tissues. Within muscle tissue this includes increasing glycogen, fatty acid, glycerol and protein synthesis and amino acid uptake, while decreasing glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism and amino acid output.
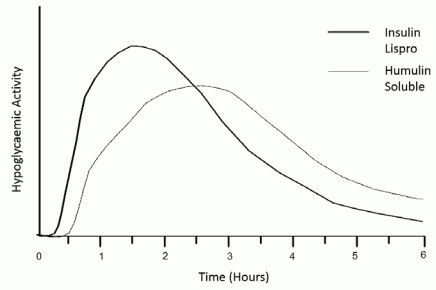
Insulin lispro has a rapid onset of action (approximately 15 minutes), thus allowing it to be given closer to a meal (within zero to 15 minutes of the meal) when compared to soluble insulin (30 to 45 minutes before). Insulin lispro takes effect rapidly and has a shorter duration of activity (2 to 5 hours) when compared to soluble insulin.
Clinical trials in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes have demonstrated reduced postprandial hyperglycaemia with insulin lispro compared to soluble human insulin.
As with all insulin preparations, the time course of insulin lispro action may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and is dependent on dose, site of injection, blood supply, temperature and physical activity. The typical activity profile following subcutaneous injection is illustrated below.
The above representation reflects the relative amount of glucose over time required to maintain the subject's whole blood glucose concentrations near fasting levels and is an indicator of the effect of these insulins on glucose metabolism over time.
Clinical trials have been performed in children (61 patients aged 2 to 11) and children and adolescents (481 patients aged 9 to 19 years), comparing insulin lispro to human soluble insulin. The pharmacodynamic profile of insulin lispro in children is similar to that seen in adults.
When used in subcutaneous infusion pumps, treatment with insulin lispro has been shown to result in lower glycosylated haemoglobin levels compared to soluble insulin. In a double-blind, crossover study, the reduction in glycosylated haemoglobin levels after 12 weeks dosing was 0.37 percentage points with insulin lispro, compared to 0.03 percentage points for soluble insulin (p=0.004).
In patients with type 2 diabetes on maximum doses of sulphonyl urea agents, studies have shown that the addition of insulin lispro significantly reduces HbA1c compared to sulphonyl urea alone. The reduction of HbA1c would also be expected with other insulin products e.g. soluble or isophane insulins.
Clinical trials in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes have demonstrated a reduced number of episodes of nocturnal hypoglycaemia with insulin lispro compared to soluble human insulin. In some studies, reduction of nocturnal hypoglycaemia was associated with increased episodes of daytime hypoglycaemia.
The glucodynamic response to insulin lispro is not affected by renal or hepatic function impairment. Glucodynamic differences between insulin lispro and soluble human insulin, as measured during a glucose clamp procedure, were maintained over a wide range of renal function.
Insulin lispro has been shown to be equipotent to human insulin on a molar basis but its effect is more rapid and of a shorter duration.
Pharmacokinetic properties
The pharmacokinetics of insulin lispro reflect a compound that is rapidly absorbed, and achieves peak blood levels 30 to 70 minutes following subcutaneous injection. When considering the clinical relevance of these kinetics, it is more appropriate to examine the glucose utilisation curves (as discussed in 5.1).
Insulin lispro maintains more rapid absorption when compared to soluble human insulin in patients with renal impairment. In patients with type 2 diabetes over a wide range of renal function the pharmacokinetic differences between insulin lispro and soluble human insulin were generally maintained and shown to be independent of renal function. Insulin lispro maintains more rapid absorption and elimination when compared to soluble human insulin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Preclinical safety data
In in vitro tests, including binding to insulin receptor sites and effects on growing cells, insulin lispro behaved in a manner that closely resembled human insulin. Studies also demonstrate that the dissociation of binding to the insulin receptor of insulin lispro is equivalent to human insulin. Acute, one month and twelve month toxicology studies produced no significant toxicity findings.
Insulin lispro did not induce fertility impairment, embryotoxicity or teratogenicity in animal studies.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.