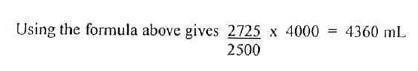JEANATOPE Solution for injection Ref.[10321] Active ingredients: Iodine ¹²⁵I human albumin
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2020
3. Indications and Usage
Jeanotope I-125 is indicated for use in the determination of total blood and plasma volume.
10. Dosage and Administration
Radioiodinated serum albumin is administered intravenously. When a procedure such as a blood volume determination is to be repeated, the total dosage administered in any one week should not exceed 7.4 megabecquerels (200 microcuries).
To minimise the uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid, prior administration of Lugol's Solution (Strong Iodine Solution USP) may be used. Ten drops of Lugol's Solution three times a daily, beginning at least 24 hours before administration of Iodinated Serum Albumin I-125 and continuing for one or two weeks thereafter, is a suitable dose.
Complete assay data for each vial are provided on the container.
Note: The expiration date given on the container pertains to the biologic properties of the material and not to the radioactivity label, it is important to make certain that the radioactivity in the dose at the time of administration is sufficient for the intended use.
Visual Inspection
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution
and container permit.
Jeanotope (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection) may be colorless to very pale yellow. Solutions with excessive coloration should not be used.
The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
Note: A shielded syringe should be used for withdrawing and injecting the Iodinated I-125 Albumin.
Total Blood and Plasma Volumes
Dosage may range from .185 to 1.85 megabecquerels (5 to 50 microcuries).
Blood Volume Determination
A. Preparation of Reference Solution:
Remove an aliquot of the contents of the vial to be used in the procedure identical in volume to the dose to be administered to the patient. Prepare a reference solution using normal saline as a diluent. The recommended dilution is 1:4000 (Dilution Factor (DF) = 4000). Determine the radioactivity concentration (net cpm/ml) of the reference solution. Care must be taken to assure that the reference solution and the blood samples (Step B3) are assayed using the same geometric configuration.
A. Administration of Dose:
- Inject the dose into a large vein in patient's arm. Measure the residual radioactivity in the syringe and needle.
- Destroy the syringe after injecting. Do not attempt to resterilize.
CAUTION: the syringe should be disposed of in accordance with the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission or Agreement State regulations pertaining to the disposal of radioactive waste. - At 5 and 15 minutes after injecting the dose, withdraw blood samples from the patient's other arm with a sterile heparinized syringe.
B. Calculation of Blood Volume:
- Take a known aliquot from each blood sample and determine radioconcentration in net cpm/mL.
- Plot the 5- and 15-minute sample counts (net cpm/mL) on semilog graph paper using the average count value of each sample and determine the radioconcentration at injection time (zero time) by drawing a straight line through the 15- and 5- minute points to zero time. The x ordinate of the graph is the sample withdrawal time and the logarithmic y ordinate is radioconcentration in net cpm/mL.
- Calculate the patient's blood volume (in mL) using the following formula:
Net cpm/mL reference solution / Net cpm/mL patient's blood sample × DF = blood volume (in mL)
Sample Blood Volume Calculations:
Volume of blood sample aliquot = 1.0 mL
Volume of reference solution aliquot = 1.0 mL
Net counts at zero time = 2500
Net counts obtained from reference solution aliquot = 2725
Serial Blood Volume Determinations
Jeanotope (Iodinated I-125 Albumin Injection) is administered in sufficiently low dosage to permit repetitions as often as required by clinical circumstances. It must be remembered that it is always necessary to correct for background radioactivity remaining in the blood from former determinations. Therefore, for each determination after the first one, a background blood sample must be taken just before the iodinated I-125 Albumin is injected.
Background Blood Sample:
- Prior to injecting Jeanotope I-125, withdraw background blood sample from large vein in patient's arm with a sterile heparinized syringe.
- Leaving needle in a patient's vein, detach syringe containing blood sample.
- Withdraw Jeanotope I-125 from the vial and administer (see instructions under Blood Volume Determination, Administration of Dose).
- Determine radioconcentration in net cpm/mL of aliquots taken from background and postinjection blood samples, and from the reference solution.
The radioconcentration (net cpm/mL) per aliquot of the background blood sample must be subtracted from the radioconcentration per aliquot of the blood sample obtained after the injection of Iodinated I-125 Albumin. The formula for calculating each blood volume determination after the first one thus becomes:
Net cpm/mL reference solution / Net cpm/mL postinjection blood sample minus Net cpm/mL background blood sample × 400 = blood volume (in mL)
Plasma Volume Determination
The procedure is essentially the same as that for blood volume determination, except that the blood sample drawn from the patient is centrifuged, the red blood cells are removed, and net cpm/mL of the plasma is determined. The formula for calculation of plasma volume, therefore is:
Net cpm/mL reference solution / Net cpm/mL patient's plasma sample × 400 = plasma volume (in mL)
Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to an average patient (70 kg) from an intravenous injection of 1.85 megabecquerels (50 microcuries) of iodinated I-125 Albumin USP are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Estimated Absorbed Radiation Doses:
| Tissue | Rads |
|---|---|
| Blood | .15 |
| Whole-body | .025 - .035 |
Method of Calculation: Hine GJ, Johnston RE: Absorbed Doses from Radionuclides, J. Nucl Med 11:468-469, 1970.
For doses of 2.775, 5.55, 18.5 and 27.75 megabecquerels (75, 150, 500 and 750 microcuries), the estimated absorbed doses are 1.5, 3, 10 and 15 times the number of rads given respectively.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.