OCTANINE Powder for solution for injection Ref.[51133] Active ingredients: Coagulation factor IX
Source: Medicines Authority (MT) Revision Year: 2020 Publisher: Octapharma (IP) SPRL, Allée de la Recherche 65, 1070 Anderlecht, Belgium
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency).
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of haemophilia.
Previously untreated patients
The safety and efficacy of OCTANINE in previously untreated patients have not yet been established.
Treatment monitoring
During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor IX levels is advised to guide the dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. Individual patients may vary in their response to factor IX, demonstrating different half-lives and recoveries.
Dose based on bodyweight may require adjustment in underweight or overweight patients. In the case of major surgical interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation analysis (plasma factor IX activity) is indispensable.
Posology
Dose and duration of the substitution therapy depend on the severity of the factor IX deficiency, on the location and extent of the bleeding and on the patient's clinical condition.
The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an International Standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of normal human plasma.
On demand treatment
The calculation of the required dosage of factor IX is based on the empirical finding that 1 International Unit (IU) factor IX per kg body weight raises the plasma factor IX activity by 1 % of normal activity. The required dosage is determined using the following formula:
Required units = body weight (kg) x desired factor IX rise (%) (IU/dl) x 0.8
The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the clinical effectiveness in the individual case.
In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor IX activity should not fall below the given plasma activity level (in % of normal) in the corresponding period. The following table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery:
| Degree of haemorrhage / Type of surgical procedure | Factor IX level required (%) (IU/dl) | Frequency of doses (hours) / Duration of therapy (days) |
|---|---|---|
| Haemorrhage | ||
| Early haemarthrosis, muscle bleeding or oral bleeding | 20-40 | Repeat every 24 hours. At least 1 day, until the bleeding episode as indicated by pain is resolved or healing is achieved. |
| More extensive haemarthrosis, muscle bleeding or haematoma | 30-60 | Repeat infusion every 24 hours for 3-4 days or more until pain and acute disability are resolved. |
| Life-threatening haemorrhages | 60-100 | Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until threat is resolved. |
| Surgery | ||
| Minor Surgery including tooth extraction | 30-60 | Every 24 hours, at least 1 day, until healing is achieved. |
| Major Surgery | 80–100 (pre- and/post- operative) | Repeat infusion every 8-24 hours until adequate wound healing, then therapy for at least another 7 days to maintain a factor IX activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl). |
Prophylaxis
For long term prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia B, the usual doses are 20 to 40 IU of factor IX per kilogram of body weight at intervals of 3 to 4 days. In some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
Continuous infusion
There is not enough data available to recommend continous infusion of OCTANINE in surgical procedures.
Paediatric Population
In the study conducted in 25 children under 6 years of age, the median dose administered per exposure day was similar for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding, i.e. 35 to 40 IU/kg BW.
Method of administration
Intravenous use. It is recommended not to administer more than 2-3 ml per minute. For instructions on reconstitution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.
4.9. Overdose
No cases of overdose have been reported.
6.3. Shelf life
2 years.
Biochemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 72 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the reconstituted product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the users and would not be recommended for longer than 8 hours stored at room temperature (25°C).
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Do not store above 25°C.
Do not freeze.
Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions after reconstitution of the medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
OCTANINE comes as a combination package consisting of two cartons held together with a plastic film.
OCTANINE 500 IU:
Carton 1: powder in a 30 ml vial (type I glass), with a stopper (chlorobutyl or bromobutyl rubber) and a flip off cap (aluminium); package leaflet.
+
Carton 2: 5 ml of solvent (water for injections) (type I or type II glass), with a stopper (chlorobutyl or bromobutyl rubber) and a flip off cap (aluminium).
OCTANINE 1000 IU:
Carton 1: powder in a 30 ml vial (type I glass), with a stopper (chlorobutyl or bromobutyl rubber) and a flip off cap (aluminium); package leaflet.
+
Carton 2: 10 ml of solvent (water for injections) (type I or type II glass), with a stopper (chlorobutyl or bromobutyl rubber) and a flip off cap (aluminium).
Carton 2 also contains the following medical devices:
- 1 disposable syringe
- 1 transfer set Mix2VialTM
- 1 infusion set (butterfly)
- 2 alcohol swabs
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Please read all the instructions and follow them carefully!
Do not use OCTANINE after expiry date given on the label and carton.
During the procedure described below, sterility must be maintained!
The solution in the syringe should be clear or slightly opalescent. Do not inject solutions that are cloudy or have deposits.
Use the prepared solution immediately, to prevent microbial contamination.
Only use the injection set provided. The use of other injection/infusion equipment can cause additional risks and treatment failure.
Instructions for preparing the solution:
1. Do not use the product directly from the refrigerator. Allow the solvent and the powder in the closed vials to reach room temperature.
2. Remove the flip off caps from both vials and clean the rubber stoppers with one of the provided alcohol swabs.
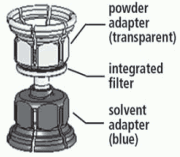
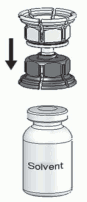
3. The Mix2vial is depicted in Fig. 1. Place the solvent vial on an even surface and hold it firmly. Take the Mix2Vial and turn it upside down. Place the blue part of the Mix2Vial on top of the solvent vial and press firmly down until it snaps (Fig. 2 + 3).
Fig. 1:
Fig. 2:
Fig. 3:
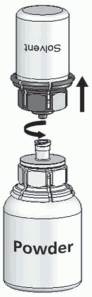
4. Place the powder vial on an even surface and hold it firmly. Take the solvent vial with the attached Mix2Vial and turn it upside down. Place the transparent part on top of the powder vial and press firmly down until it snaps (Fig. 4). The solvent flows automatically into the powder vial.
Fig. 4:
5. With both vials still attached, gently swirl the powder vial until the product is dissolved.
The dissolving is completed in less than 10 minutes at room temperature.Slight foaming might occur during preparation. Unscrew the Mix2Vial into two parts (Fig. 5). Foaming will disappear.
Fig. 5:
Dispose the empty solvent vial with the blue part of the Mix2Vial.
Instructions for Injection:
As a precaution, your pulse rate should be taken before and during the injection. If a marked increase in your pulse rate occurs, reduce the injection speed or interrupt the administration for a short time.
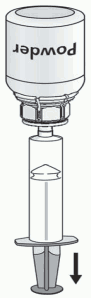
1. Attach the syringe to the transparent part of the Mix2Vial. Turn the vial upside down and draw the solution into the syringe (Fig. 6).
The solution in the syringe should be clear or slightly pearly shimmery.
Once the solution has been transferred, firmly hold the plunger of the syringe (keeping it facing down) and remove the syringe from the Mix2Vial (Fig. 7). Dispose the Mix2Vial and the empty vial.
Fig. 6:
Fig. 7:
2. Clean the chosen injection site with one of the provided alcohol swabs.
3. Attach the provided injection needle to the syringe.
4. Insert the injection needle into the chosen vein. If you have used a tourniquet to make the vein easier to see, this tourniquet should be released before you start injecting OCTANINE. No blood must flow into the syringe due to the risk of formation of fibrin clots.
5. Inject the solution into the vein at a slow speed, not faster than 2-3 ml per minute.
If you use more than one vial of OCTANINE powder for one treatment, you may use the same injection needle and syringe again. The Mix2Vial is for single use only.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.