ROLVEDON Solution for injection Ref.[107270] Active ingredients: Eflapegrastim
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2023
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Eflapegrastim-xnst is a recombinant human granulocyte growth factor that binds to G-CSF receptors on myeloid progenitor cells and neutrophils, triggering signaling pathways that control cell differentiation, proliferation, migration and survival.
12.2. Pharmacodynamics
Eflapegrastim-xnst has been shown to elevate neutrophil counts in healthy subjects and in cancer patients. Absolute neutrophil count (ANC), Cmaxand area under the effect curve (AUEClast) increased with increasing doses of eflapegrastim-xnst in a linear, but less than dose-proportional, manner over a dose range of 45 to 350 mcg/kg.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of eflapegrastim-xnst was studied in healthy subjects and patients with breast cancer. After subcutaneous (SC) dosing, the pharmacokinetics of eflapegrastim-xnst was nonlinear and exposure increases were not dose-proportional over the dose range of 45 to 350 mcg/kg.
Absorption
The median Tmax of eflapegrastim-xnst is 25 hours (6 to 144 hours) in patients with breast cancer following administration of the recommended dosage.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of eflapegrastim-xnst is 1.44 L.
Elimination
The geometric mean half-life of eflapegrastim-xnst in patients with breast cancer is 36.4 hours (Range: 16.1 to 115 hours) during Cycle 1. Eflapegrastim-xnst clearance decreased with increasing doses following single dose administration, suggesting target-mediated clearance of eflapegrastim-xnst by neutrophils. Following repeat administration, clearance increased in Cycle 3 as compared to Cycle 1, potentially due to the subsequent increase in neutrophils. In in vitro studies, the IgG4 Fc fragment in eflapegrastim-xnst binds to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), facilitating the FcRn-mediated transcytosis of eflapegrastim-xnst.
Metabolism
Eflapegrastim-xnst is expected to be metabolized by endogenous degradation following receptor-mediated internalization by cells bearing the G-CSF receptor.
Excretion
Eflapegrastim-xnst was not detected in urine.
Drug Interaction Studies
No studies evaluating the drug interaction potential of eflapegrastim-xnst have been conducted.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed with eflapegrastim-xnst.
Eflapegrastim-xnst was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a standard battery of genotoxicity tests (bacterial mutagenicity (Ames), Chinese hamster ovary cells chromosomal aberration, rat bone marrow micronucleus).
Eflapegrastim-xnst did not affect reproductive performance or fertility in male or female rats at weekly doses up to 7 times the clinical exposure at the maximum recommended dose of 13.2 mg.
14. Clinical Studies
Patients with Cancer Receiving Myelosuppressive Chemotherapy
The efficacy of Rolvedon to decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs was evaluated in two 1:1 randomized, open-label, active-controlled non-inferiority studies of similar design (Study 1 [NCT02643420] and Study 2 [NCT02953340]) that enrolled a total of 643 patients with early-stage breast cancer. Docetaxel 75 mg/m² and cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m² (TC) were administered intravenously every 21 days (on Day 1 of each cycle) for up to 4 cycles. A fixed dose of Rolvedon 13.2 mg/0.6 mL or pegfilgrastim (6 mg/0.6 mL) was administered subcutaneously on Day 2 of each cycle after TC chemotherapy.
The median age of patients enrolled in the two randomized studies was 60 years (Range: 24 to 88), the majority of patients were female (>99%), 77% were White and 12% were Black or African American.
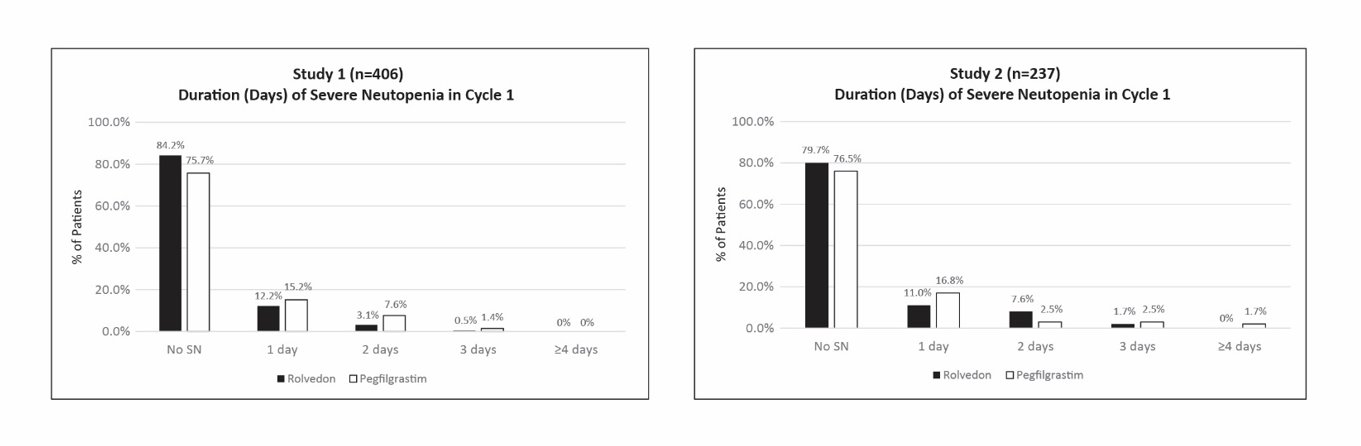
Study 1 enrolled 406 patients; 196 patients to the Rolvedon arm and 210 patients to the pegfilgrastim arm. Study 2 enrolled 237 patients; 118 patients to the Rolvedon arm and 119 patients to the pegfilgrastim arm. Efficacy for both trials was based on the duration of severe neutropenia (DSN) in Cycle 1.
Efficacy results are shown in Table 2. In both studies, Rolvedon was non-inferior to pegfilgrastim. The distributions of the severe neutropenia events in percentage from Cycle 1 for Study 1 and Study 2 are presented in Figure 1.
Table 2. Duration of Severe Neutropenia (DSN) in Cycle 1 (Study 1 and Study 2):
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolvedon(n=196) | Pegfilgrastim (n=210) | Rolvedon (n=118) | Pegfilgrastim (n=119) | |
| Mean DSN (SD) (Days) | 0.20 (0.503) | 0.35 (0.683) | 0.31 (0.688) | 0.39 (0.949) |
| Median DSN (Range) (Days) | 0 (0, 3) | 0 (0, 3) | 0 (0, 3) | 0 (0, 7) |
| Difference in DSN (Days) | -0.148 | -0.073 | ||
| *95% Confidence Intervala | -0.265, -0.033 | -0.292, 0.129 | ||
a Confidence intervals were obtained using 2.5 percentile and 97.5 percentile of the 100,000 bootstrap samples with treatment as stratification factor.
* The non-inferiority of Rolvedon to pegfilgrastim was to be declared if the upper bound of 95% CI of the difference in mean DSN between the treatment arms was <0.62 days.
Figure 1. Duration of Severe Neutropenia (DSN) by Day in Cycle 1 (Study 1 and Study 2):
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.