SKELAXIN Tablet Ref.[10328] Active ingredients:
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2018
2. Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of metaxalone in humans has not been established, but may be due to general central nervous system (CNS) depression. Metaxalone has no direct action on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate, or the nerve fiber.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of metaxalone have been evaluated in healthy adult volunteers after single dose administration of SKELAXIN under fasted and fed conditions at doses ranging from 400 mg to 800 mg.
Absorption
Peak plasma concentrations of metaxalone occur approximately 3 hours after a 400 mg oral dose under fasted conditions. Thereafter, metaxalone concentrations decline log-linearly with a terminal half-life of 9.0 ± 4.8 hours. Doubling the dose of SKELAXIN from 400 mg to 800 mg results in a roughly proportional increase in metaxalone exposure as indicated by peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC). Dose proportionality at doses above 800 mg has not been studied. The absolute bioavailability of metaxalone is not known.
The single-dose pharmacokinetic parameters of metaxalone in two groups of healthy volunteers are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Mean (%CV) Metaxalone Pharmacokinetic Parameters:
| Dose (mg) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC∞ (ng∙h/mL) | t½(h) | CL/F (L/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400* | 983 (53) | 3.3 (35) | 7479 (51) | 9.0 (53) | 68 (50) |
| 800† | 1816 (43) | 3.0 (39) | 15044 (46) | 8.0 (58) | 66 (51) |
* Subjects received 1×400 mg tablet under fasted conditions (N=42)
† Subjects received 2×400 mg tablets under fasted conditions (N=59)
Food Effects
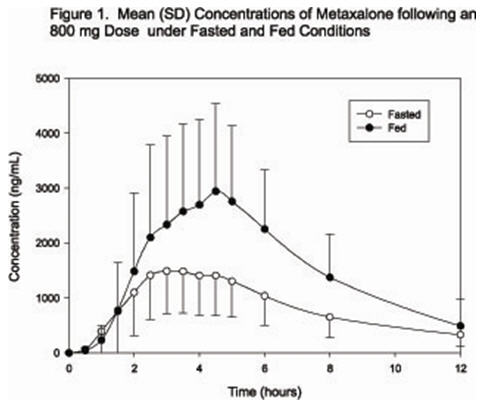
A randomized, two-way, crossover study was conducted in 42 healthy volunteers (31 males, 11 females) administered one 400 mg SKELAXIN tablet under fasted conditions and following a standard high-fat breakfast. Subjects ranged in age from 18 to 48 years (mean age = 23.5 ± 5.7 years). Compared to fasted conditions, the presence of a high fat meal at the time of drug administration increased Cmax by 177.5% and increased AUC (AUC0–t, AUC∞) by 123.5% and 115.4%, respectively. Time-to-peak concentration (Tmax) was also delayed (4.3 h versus 3.3 h) and terminal half-life was decreased (2.4 h versus 9.0 h) under fed conditions compared to fasted.
In a second food effect study of similar design, two 400 mg SKELAXIN tablets (800 mg) were administered to healthy volunteers (N=59, 37 males, 22 females), ranging in age from 18–50 years (mean age = 25.6± 8.7 years). Compared to fasted conditions, the presence of a high fat meal at the time of drug administration increased Cmax by 193.6% and increased AUC (AUC0–t, AUC∞) by 146.4% and 142.2%, respectively. Time-to-peak concentration (Tmax) was also delayed (4.9 h versus 3.0 h) and terminal half-life was decreased (4.2 h versus 8.0 h) under fed conditions compared to fasted conditions. Similar food effect results were observed in the above study when one SKELAXIN 800 mg tablet was administered in place of two SKELAXIN 400 mg tablets. The increase in metaxalone exposure coinciding with a reduction in half-life may be attributed to more complete absorption of metaxalone in the presence of a high fat meal (Figure 1).
Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
Although plasma protein binding and absolute bioavailability of metaxalone are not known, the apparent volume of distribution (V/F ~ 800 L) and lipophilicity (log P=2.42) of metaxalone suggest that the drug is extensively distributed in the tissues. Metaxalone is metabolized by the liver and excreted in the urine as unidentified metabolites. Hepatic Cytochrome P450 enzymes play a role in the metabolism of metaxalone. Specifically, CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 appear to metabolize metaxalone.
Metaxalone does not significantly inhibit major CYP enzymes such as CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4. Metaxalone does not significantly induce major CYP enzymes such as CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4 in vitro.
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Age
The effects of age on the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone were determined following single administration of two 400 mg tablets (800 mg) under fasted and fed conditions. The results were analyzed separately, as well as in combination with the results from three other studies. Using the combined data, the results indicate that the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone are significantly more affected by age under fasted conditions than under fed conditions, with bioavailability under fasted conditions increasing with age.
The bioavailability of metaxalone under fasted and fed conditions in three groups of healthy volunteers of varying age is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Mean (%CV) Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following Single Administration of Two 400 mg SKELAXIN Tablets (800 mg) under Fasted and Fed Conditions:
| Younger Volunteers | Older Volunteers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 25.6 ± 8.7 | 39.3 ± 10.8 | 71.5 ± 5.0 | |||
| N | 59 | 21 | 23 | |||
| Food | Fasted | Fed | Fasted | Fed | Fasted | Fed |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1816 (43) | 3510 (41) | 2719 (46) | 2915 (55) | 3168 (43) | 3680 (59) |
| Tmax (h) | 3.0 (39) | 4.9 (48) | 3.0 (40) | 8.7 (91) | 2.6 (30) | 6.5 (67) |
| AUC0–t (ng∙h/mL) | 14531 (47) | 20683 (41) | 19836 (40) | 20482 (37) | 23797 (45) | 24340 (48) |
| AUC∞ (ng∙h/mL) | 15045 (46) | 20833 (41) | 20490 (39) | 20815 (37) | 24194 (44) | 24704 (47) |
Gender
The effect of gender on the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone was assessed in an open label study, in which 48 healthy adult volunteers (24 males, 24 females) were administered two SKELAXIN 400 mg tablets (800 mg) under fasted conditions. The bioavailability of metaxalone was significantly higher in females compared to males as evidenced by Cmax (2115 ng/mL versus 1335 ng/mL) and AUC∞ (17884 ng∙h/mL versus 10328 ng∙h/mL). The mean half-life was 11.1 hours in females and 7.6 hours in males. The apparent volume of distribution of metaxalone was approximately 22% higher in males than in females, but not significantly different when adjusted for body weight. Similar findings were also seen when the previously described combined dataset was used in the analysis.
Hepatic / Renal Insufficiency
The impact of hepatic and renal disease on the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone has not been determined. In the absence of such information, SKELAXIN should be used with caution in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment.
6.6. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of metaxalone has not been determined.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.