SUFENTA Solution for injection / infusion Ref.[50458] Active ingredients: Sufentanil
Source: Health Products Regulatory Authority (ZA) Revision Year: 2021 Publisher: Piramal Critical Care (Pty) Ltd, Office 2, Ground Floor, Kiepersol House, Stonemill Office Park, 300 Acacia Road, Darrenwood 2194
4.1. Therapeutic indications
SUFENTA administered intravenously in adults is indicated:
- as an analgesic adjunct during induction and maintenance of balanced general anaesthesia
- as an anaesthetic agent for induction and maintenance of anaesthesia in patients undergoing major surgical procedures, requiring endotracheal intubation and ventilation.
SUFENTA administered by epidural route in adults is indicated:
- for post-operative management of pain following general surgery, thoracic or orthopaedic procedures and caesarean sections
- as an analgesic adjunct to epidural bupivacaine with or without adrenaline (epinephrine) during labour and vaginal deliveries.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
SUFENTA injection should be administered only by persons specifically trained in the use of intravenous anaesthetics and management of the respiratory effects of potent opioids. Ensure that an opioid antagonist, resuscitative and intubation equipment, and oxygen are readily available.
The dosage of SUFENTA should be individualised. Factors to be considered in determining the dose are age, body mass, physical status, underlying pathological conditions, use of other medicines, and type of surgical procedure and anaesthesia. The effect of the initial dose should be taken into account in determining supplemental doses.
In obese patients, the dosage of SUFENTA should be determined on the estimated lean body mass.
Administration as an analgesic adjunct in general anaesthesia to nitrous oxide/oxygen
Droperidol may be given to reduce the incidence of nausea and vomiting.
INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION
Adults
Initial dose: 1–8 µg/kg administered with nitrous oxide/oxygen. The duration of action is 1–8 hours depending on the dose.
Maintenance dose: 0,1–0,5 µg/kg as needed when movement and/or changes in vital signs indicate surgical stress or lightening of analgesia.
Supplemental dosages should be individualised and adjusted to the remaining operative time anticipated.
Special populations for intravenous administration
Elderly (65 years of age and older)
The dose should be reduced in the elderly and in debilitated patients.
Patients with severe renal impairment and end-stage renal failure
The dosage of SUFENTA should be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment and end-stage renal failure.
SUFENTA should be titrated with caution in these patients.
Such patients also require prolonged post-operative monitoring.
Paediatric population
Children ≤1 month (neonates): Due to the large variability of pharmacokinetic parameters in neonates, no dosing recommendations can be made (see section 4.4 and 5.2).
Children >1 month: Induction of anaesthesia SUFENTA can be administered as a slow bolus injection of 0,2–0,5 µg/kg over 30 seconds or longer in combination with an anaesthetic induction medicine. For major surgery (e.g. cardiac surgery) doses up to 1 µg/kg can be administered.
Maintenance of anaesthesia in ventilated patients
SUFENTA can be administered as part of balanced anaesthesia. The dosage depends on the dose of concomitant anaesthetic medicines, type and duration of surgery. An initial dose of 0,3–2 µg/kg administered by slow bolus injection over at least 30 seconds may be followed by additional boluses of 0,1–1 µg/kg as required, up to a total maximum of 5 µg/kg in cardiac surgery.
EPIDURAL ADMINISTRATION
Proper placement of a needle or catheter in the epidural space should be verified before SUFENTA is injected to assure that unintentional intravascular or intrathecal administration does not occur.
Unintentional intravascular injection of SUFENTA could result in potentially serious overdose, including acute truncal muscular rigidity and apnoea. Unintentional intrathecal injection of the full sufentanil, local anaesthetic epidural doses and volume could produce effects of high spinal anaesthesia, including prolonged paralysis, acute truncal muscular rigidity that may make manual ventilation difficult, apnoea and delayed recovery. If analgesia is inadequate, the placement and integrity of the catheter should be verified prior to administration of any additional epidural medications. SUFENTA should be administered by slow injection.
With epidural administration, caution should be exercised in the presence of respiratory depression and in the presence of foetal distress.
Epidural administration requires that the patient should be in a high care environment with continuous supervision.
The patient should be closely monitored for at least 2 hours after each dose, as early respiratory depression may occur.
Post-operative management of pain – Adults
An initial dose of 30–50 µg may be expected to provide adequate pain relief for up to 4–6 hours. Additional bolusses of 25 µg may be administered if there is evidence of lightening of analgesia. There should be a minimum interval of 1 hour between doses.
Analgesic adjunct during labour and vaginal deliveries
The recommended dosage is 10–15 µg administered with 10 mL bupivacaine 0,125 % with or without epinephrine (adrenaline). SUFENTA and bupivacaine should be mixed together before administration. Doses can be repeated twice (for a total of three doses) at not less than one-hour intervals until delivery.
Use as analgesic adjunct
In patients undergoing general surgery, doses of SUFENTA of 0,5–5 µg/kg provide intense analgesia, reducing the sympathetic response to surgical stimulation and preserving cardiovascular stability. The duration of activity is dose dependent. A dose of 0,5 µg/kg may be expected to last 50 minutes. Supplemental doses of 10–25 µg should be individually adjusted to the needs of each patient and to the anticipated remaining operation time.
Use as anaesthetic medicine
When used in doses of ≥8 µg/kg, SUFENTA produces sleep and maintains a dose-related profound level of analgesia without the use of additional anaesthetic medicines. In addition, sympathetic and hormonal responses to surgical stimuli are attenuated. Supplementary doses of 25 – 50 µg generally suffice to maintain cardiovascular stability during anaesthesia.
Special populations for epidural administration
Elderly patients (65 years of age and older)
The dose should be reduced in the elderly and in debilitated patients.
Paediatric population
SUFENTA must be administered to children epidurally only by anaesthesiologists specifically trained in paediatric epidural anaesthesia and in management of respiratory depressant effects of opioids. Appropriate resuscitation equipment, including airway securing devices and an opioid antagonist must be readily available.
aediatric patients must be monitored for signs of respiratory depression for at least 2 hours after epidural administration of SUFENTA.
The safety and efficacy of epidural use of SUFENTA in paediatric patients has not been established, as limited data are available.
Children <1 year: No data are available for epidural administration of SUFENTA to newborns and infants younger than 3 months, and limited data are available for children between 3 months and 1 year (see section 5.1). Safety and efficacy of SUFENTA in children younger than 1 year have not been established (see sections 4.4 and 5.1). Therefore, no dosing recommendations can be made for children in this age group.
Children ≥1 year: A single bolus dose of 0,25–0,75 µg/kg SUFENTA given intra-operatively provided pain relief for a period, which ranged from 1 to 12 hours in clinical trials. The duration of effective analgesia is influenced by the surgical procedure and concomitant use of epidural amide local anaesthetic medicines.
Method of administration
Epidural administration
Proper placement of a needle or catheter in the epidural space should be verified before SUFENTA is injected.
4.9. Overdose
Signs and symptoms
An overdose of SUFENTA manifests itself as an extension of its pharmacological actions. Depending on the individual sensitivity, the clinical picture is determined primarily by the degree of respiratory depression, which varies from bradypnoea to apnoea.
Treatment
In the presence of hypoventilation or apnoea, oxygen should be administered, and respiration should be assisted or controlled as indicated. A specific opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, should be used as indicated to control respiratory depression. This does not preclude the use of more immediate countermeasures. The respiratory depression may last longer than the effect of the antagonist; additional doses of the latter may therefore be required.
If depressed respiration is associated with muscular rigidity, an intravenous neuromuscular blocking medicine might be required to facilitate assisted or controlled respiration. The patient should be carefully monitored, body warmth and adequate fluid intake should be maintained. If hypotension is severe or if it persists, the possibility of hypovolaemia should be considered, and if present, it should be controlled with appropriate parenteral fluid administration.
6.3. Shelf life
36 months.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Store at or below 25°C. Protect from light.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
Cartons containing: 5 × 2 mL and 5 × 10 mL ampoules.
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
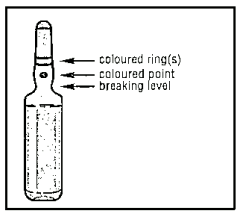
Wear gloves while opening the ampoule.
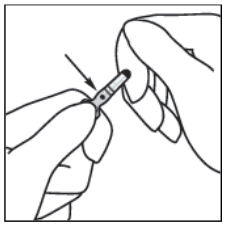
1. Hold the ampoule between the thumb and index finger, leaving the tip of the ampoule free.
2. With the other hand, hold the tip of the ampoule by putting the index finger against the neck of the ampoule, and the thumb on the coloured point in parallel to the identification ring(s).
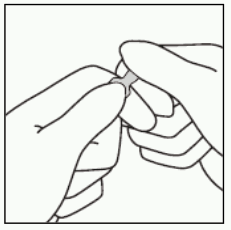
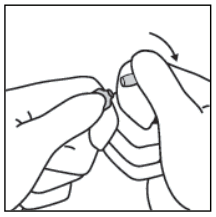
3. Keeping the thumb on the point, sharply break the tip of the ampoule while firmly holding the other part of the ampoule in the hand.
Accidental dermal exposure should be treated by rinsing the affected area with water. Avoid use of soap, alcohol, and other cleaning materials that may cause chemical or physical abrasions to the skin.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.