Oxaliplatin Other names: Oxaloplatine
Chemical formula: C₈H₁₂N₂O₄Pt Molecular mass: 397.294 g/mol PubChem compound: 6857599
Mechanism of action
Oxaliplatin is an antineoplastic active substance belonging to a new class of platinum-based compounds in which the platinum atom is complexed with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane (“DACH”) and an oxalate group. Oxaliplatin is a single enantiomer, the Cis-[oxalato(trans-l-1,2-DACH) platinum].
Pharmacodynamic properties
Oxaliplatin exhibits a wide spectrum of both in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo antitumour activity in a variety of tumour model systems including human colorectal cancer models. Oxaliplatin also demonstrates in vitro and in vivo activity in various cisplatin resistant models.
A synergistic cytotoxic action has been observed in combination with 5-fluorouracil both in vitro and in vivo. Studies on the mechanism of action of oxaliplatin, although not completely elucidated, show that the aqua-derivatives resulting from the biotransformation of oxaliplatin, interact with DNA to form both inter and intra-strand cross-links, resulting in the disruption of DNA synthesis leading to cytotoxic and antitumour effects.
Pharmacokinetic properties
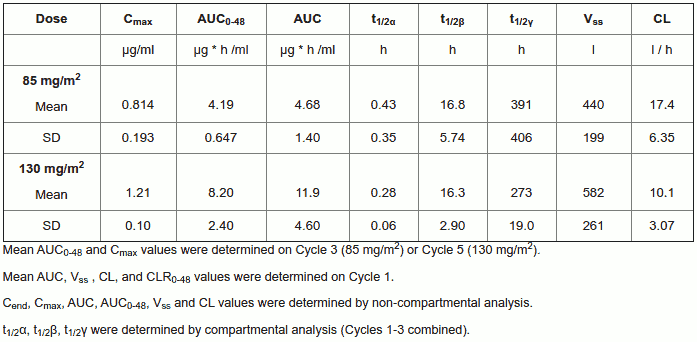
The pharmacokinetics of individual active compounds have not been determined. The pharmacokinetics of ultrafiltrable platinum, representing a mixture of all unbound, active and inactive platinum species, following a two-hour infusion of oxaliplatin at 130 mg/m² every three weeks for 1 to 5 cycles and oxaliplatin at 85 mg/m² every two weeks for 1 to 3 cycles are as follows:
Summary of Platinum Pharmacokinetic Parameter Estimates in Ultrafiltrate Following Multiple Doses of Oxaliplatin at 85 mg/m² Every Two Weeks or at 130 mg/m² Every Three Weeks
At the end of a 2-hour infusion, 15% of the administered platinum is present in the systemic circulation, the remaining 85 % being rapidly distributed into tissues or eliminated in the urine. Irreversible binding to red blood cells and plasma, results in half-lives in these matrices that are close to the natural turnover of red blood cells and serum albumin. No accumulation was observed in plasma ultrafiltrate following 85 mg/m² every two weeks or 130 mg/m² every three weeks and steady state was attained by Cycle one in this matrix. Inter- and intra-subject variability is generally low.
Biotransformation in vitro is considered to be the result of non-enzymatic degradation and there is no evidence of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of the diaminocyclohexane (DACH) ring.
Oxaliplatin undergoes extensive biotransformation in patients, and no intact active substance was detectable in plasma ultrafiltrate at the end of a 2h-infusion. Several cytotoxic biotransformation products including the monochloro-, dichloro- and diaquo-DACH platinum species have been identified in the systemic circulation together with a number of inactive conjugates at later time points.
Platinum is predominantly excreted in urine, with clearance mainly in the 48 hours following administration.
By day 5, approximately 54% of the total dose was recovered in the urine and < 3 % in the faeces.
A significant decrease in clearance from 17.6 ± 2.18 l/h to 9.95 ± 1.91 l/h in renal impairment was observed together with a statistically significant decrease in distribution volume from 330 ± 40.9 to 241 ± 36.1 l. The effect of severe renal impairment on platinum clearance has not been evaluated.
Preclinical safety data
The target organs identified in preclinical species (mice, rats, dogs, and/or monkeys) in single- and multiple-dose studies included the bone marrow, the gastrointestinal system, the kidney, the testes, the nervous system, and the heart. The target organ toxicities observed in animals are consistent with those produced by other platinum-containing medicinal products and DNA-damaging, cytotoxic medicinal products used in the treatment of human cancers with the exception of the effects produced on the heart. Effects on the heart were observed only in the dog and included electrophysiological disturbances with lethal ventricular fibrillation. Cardiotoxicity is considered specific to the dog not only because it was observed in the dog alone but also because doses similar to those producing lethal cardiotoxicity in dogs (150 mg/m²) were well-tolerated by humans. Preclinical studies using rat sensory neurons suggest that the acute neurosensory symptoms related to Oxaliplatin may involve an interaction with voltage-gated Na+ channels.
Oxaliplatin was mutagenic and clastogenic in mammalian test systems and produced embryo-fetal toxicity in rats. Oxaliplatin is considered a probable carcinogen, although carcinogenic studies have not been conducted.
Related medicines
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.