CIPROFLOXACIN Solution for infusion Ref.[6734] Active ingredients: Ciprofloxacin
Source: Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (GB) Revision Year: 2019 Publisher: Villerton Invest SA, Rue Edward Steichen 14, 2540 Luxembourg
Therapeutic indications
Ciprofloxacin 2mg/ml solution for infusion is indicated for the treatment of the following infections (see sections 4.4 and 5.1). Special attention should be paid to available information on resistance to ciprofloxacin before commencing therapy.
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Adults
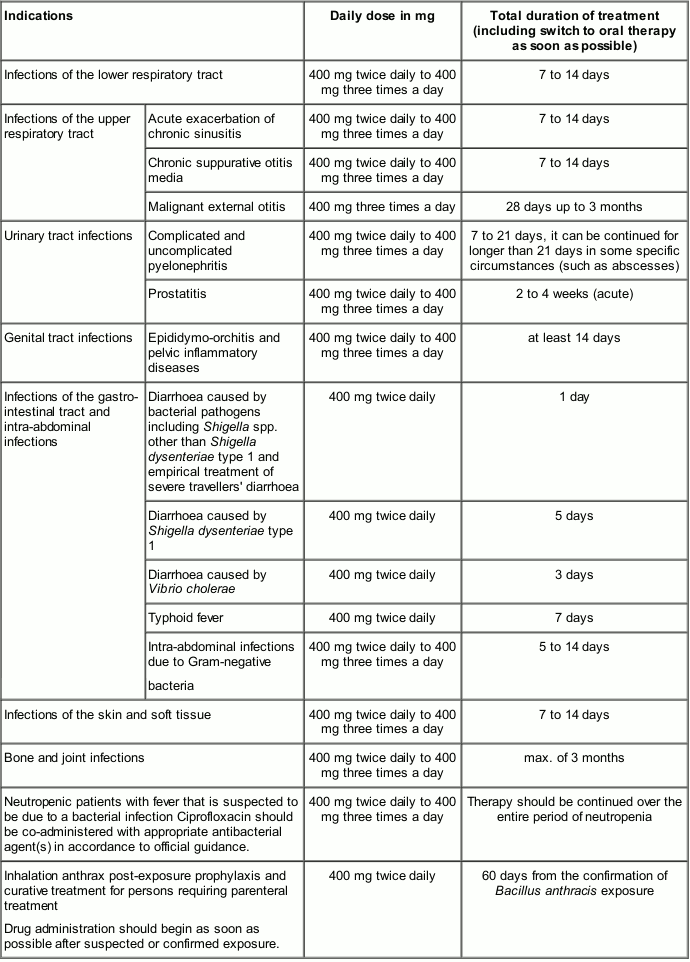
- Lower respiratory tract infections due to Gram-negative bacteria.
- Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Broncho-pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis or in bronchiectasis.
- Pneumonia.
- Chronic suppurative otitis media.
- Acute exacerbation of chronic sinusitis especially if these are caused by Gram-negative bacteria.
- Urinary tract infections.
- Genital tract infections.
- Epididymo-orchitis including cases due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease including cases due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Infections of the gastro-intestinal tract (e.g. travellers' diarrhoea).
- Intra-abdominal infections.
- Infections of the skin and soft tissue caused by Gram-negative bacteria.
- Malignant external otitis.
- Infections of the bones and joints.
- Inhalation anthrax (post-exposure prophylaxis and curative treatment).
Ciprofloxacin may be used in the management of neutropenic patients with fever that is suspected to be due to a bacterial infection.
Children and adolescents
- Broncho-pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Complicated urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis.
- Inhalation anthrax (post-exposure prophylaxis and curative treatment).
Ciprofloxacin may also be used to treat severe infections in children and adolescents when this is considered to be necessary.
Treatment should be initiated only by physicians who are experienced in the treatment of cystic fibrosis and/or severe infections in children and adolescents (see sections 4.4 and 5.1).
Posology and method of administration
The dosage is determined by the indication, the severity and the site of the infection, the susceptibility to ciprofloxacin of the causative organism(s), the renal function of the patient and, in children and adolescents the body weight.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the illness and on the clinical and bacteriological course.
After intravenous initiation of treatment, the treatment can be switched to oral treatment with tablet or suspension if clinically indicated at the discretion of the physician. IV treatment should be followed by oral route as soon as possible.
In severe cases or if the patient is unable to take tablets (e.g. patients on enteral nutrition), it is recommended to commence therapy with intravenous ciprofloxacin until a switch to oral administration is possible.
Treatment of infections due to certain bacteria (e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter or Staphylococci) may require higher ciprofloxacin doses and co-administration with other appropriate antibacterial agents.
Treatment of some infections (e.g. pelvic inflammatory disease, intra-abdominal infections, infections in neutropenic patients and infections of bones and joints) may require co-administration with other appropriate antibacterial agents depending on the pathogens involved.
Adults
Children and adolescents
| Indication | Daily dose in mg | Total duration of treatment (including switch to oral therapy as soon as possible) |
|---|---|---|
| Cystic fibrosis | 10 mg/kg body weight three times a day with a maximum of 400 mg per dose. | 10 to 14 days |
| Complicated urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis | 6 mg/kg body weight three times a day to 10 mg/kg body weight three times a day with a maximum of 400 mg per dose. | 10 to 21 days |
| Inhalation anthrax post-exposure curative treatment for persons requiring parenteral treatment. Drug administration should begin as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure. | 10 mg/kg body weight twice daily to 15 mg/kg body weight twice daily with a maximum of 400 mg per dose. | 60 days from the confirmation of Bacillus anthracis exposure |
| Other severe infections | 10 mg/kg body weight three times a day with a maximum of 400 mg per dose. | According to the type of infections |
Geriatric patients
Geriatric patients should receive a dose selected according to the severity of the infection and the patient’s creatinine clearance.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Recommended starting and maintenance doses for patients with impaired renal function:
| Creatinine Clearance [mL/min/1.73 m²] | Serum Creatinine [µmol/L] | Intravenous Dose [mg] |
|---|---|---|
| >60 | <124 | See Usual Dosage. |
| 30-60 | 124 to 168 | 200-400 mg every 12h |
| <30 | >169 | 200-400 mg every 24h |
| Patients on haemodialysis | >169 | 200-400 mg every 24h (after dialysis) |
| Patients on peritoneal dialysis | >169 | 200-400 mg every 24h |
In patients with impaired liver function no dose adjustment is required.
Dosing in children with impaired renal and/or hepatic function has not been studied.
Method of administration
Ciprofloxacin 2mg/ml solution for infusion should be checked visually prior to use. It must not be used if cloudy.
Ciprofloxacin should be administered by intravenous infusion. For children, the infusion duration is 60 minutes.
In adult patients, infusion time is 60 minutes for 400 mg of Ciprofloxacin 2mg/ml solution for infusion and 30 minutes for 200 mg of Ciprofloxacin 2mg/ml solution for infusion. Slow infusion into a large vein will minimise patient discomfort and reduce the risk of venous irritation.
The infusion solution can be infused either directly or after mixing with other compatible infusion solutions (see section 6.2).
Overdose
An overdose of 12 g has been reported to lead to mild symptoms of toxicity. An acute overdose of 16 g has been reported to cause acute renal failure. Symptoms in overdose consist of dizziness, tremor, headache, tiredness, seizures, hallucinations, confusion, abdominal discomfort, renal and hepatic impairment as well as crystalluria and haematuria. Reversible renal toxicity has been reported.
In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be implemented. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation. Apart from routine emergency measures, it is recommended to monitor renal function, including urinary pH and acidify, if required, to prevent crystalluria. Patients should be kept well hydrated.
Only a small quantity of ciprofloxacin (<10%) is eliminated by haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Shelf life
Two years.
Special precautions for storage
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Store in the original package.
Nature and contents of container
50ml, 100ml or 200ml PVC bag contained in a polypropylene/polyester- aluminium/polyester pouch. Pack sizes of 5 or 10 bags.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Since the infusion solution is photosensitive, the infusion bags should be removed from the box only immediately before use. In daylight conditions complete efficacy is guaranteed for a period of three days.
Any unused solution should be disposed off.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.