GILVEC Film-coated tablet Ref.[8027] Active ingredients: Imatinib
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2019 Publisher: Novartis Europharm Limited, Vista Building, Elm Park, Merrion Road, Dublin 4, Ireland
Therapeutic indications
Glivec is indicated for the treatment of:
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFRa rearrangement.
The effect of Glivec on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Glivec is indicated for:
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of Glivec is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with Glivec in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5.1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Posology and method of administration
Therapy should be initiated by a physician experienced in the treatment of patients with haematological malignancies and malignant sarcomas, as appropriate.
For doses other than 400 mg and 800 mg (see dosage recommendation below) a 100 mg divisible tablet is available.
For doses of 400 mg and above (see dosage recommendation below) a 400 mg tablet (not divisible) is available.
The prescribed dose should be administered orally with a meal and a large glass of water to minimise the risk of gastrointestinal irritations. Doses of 400 mg or 600 mg should be administered once daily, whereas a daily dose of 800 mg should be administered as 400 mg twice a day, in the morning and in the evening.
For patients unable to swallow the film-coated tablets, the tablets may be dispersed in a glass of still water or apple juice. The required number of tablets should be placed in the appropriate volume of beverage (approximately 50 ml for a 100 mg tablet, and 200 ml for a 400 mg tablet) and stirred with a spoon. The suspension should be administered immediately after complete disintegration of the tablet(s).
Posology for CML in adult patients
The recommended dosage of Glivec is 400 mg/day for adult patients in chronic phase CML. Chronic phase CML is defined when all of the following criteria are met: blasts <15% in blood and bone marrow, peripheral blood basophils <20%, platelets >100 × 109/l.
The recommended dosage of Glivec is 600 mg/day for adult patients in accelerated phase. Accelerated phase is defined by the presence of any of the following: blasts ≥15% but <30% in blood or bone marrow, blasts plus promyelocytes ≥30% in blood or bone marrow (providing < 30% blasts), peripheral blood basophils ≥20%, platelets <100 × 109/l unrelated to therapy.
The recommended dose of Glivec is 600 mg/day for adult patients in blast crisis. Blast crisis is defined as blasts ≥30% in blood or bone marrow or extramedullary disease other than hepatosplenomegaly.
Treatment duration: In clinical trials, treatment with Glivec was continued until disease progression. The effect of stopping treatment after the achievement of a complete cytogenetic response has not been investigated.
Dose increases from 400 mg to 600 mg or 800 mg in patients with chronic phase disease, or from 600 mg to a maximum of 800 mg (given as 400 mg twice daily) in patients with accelerated phase or blast crisis may be considered in the absence of severe adverse drug reaction and severe non-leukaemia-related neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the following circumstances: disease progression (at any time); failure to achieve a satisfactory haematological response after at least 3 months of treatment; failure to achieve a cytogenetic response after 12 months of treatment; or loss of a previously achieved haematological and/or cytogenetic response. Patients should be monitored closely following dose escalation given the potential for an increased incidence of adverse reactions at higher dosages.
Posology for CML in children
Dosing for children should be on the basis of body surface area (mg/m²). The dose of 340 mg/m² daily is recommended for children with chronic phase CML and advanced phase CML (not to exceed the total dose of 800 mg). Treatment can be given as a once daily dose or alternatively the daily dose may be split into two administrations – one in the morning and one in the evening. The dose recommendation is currently based on a small number of paediatric patients (see sections 5.1 and 5.2). There is no experience with the treatment of children below 2 years of age.
Dose increases from 340 mg/m² daily to 570 mg/m² daily (not to exceed the total dose of 800 mg) may be considered in children in the absence of severe adverse drug reaction and severe non-leukaemia- related neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the following circumstances: disease progression (at any time); failure to achieve a satisfactory haematological response after at least 3 months of treatment; failure to achieve a cytogenetic response after 12 months of treatment; or loss of a previously achieved haematological and/or cytogenetic response. Patients should be monitored closely following dose escalation given the potential for an increased incidence of adverse reactions at higher dosages.
Posology for Ph+ ALL in adult patients
The recommended dose of Glivec is 600 mg/day for adult patients with Ph+ ALL. Haematological experts in the management of this disease should supervise the therapy throughout all phases of care.
Treatment schedule: On the basis of the existing data, Glivec has been shown to be effective and safe when administered at 600 mg/day in combination with chemotherapy in the induction phase, the consolidation and maintenance phases of chemotherapy (see section 5.1) for adult patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL. The duration of Glivec therapy can vary with the treatment programme selected, but generally longer exposures to Glivec have yielded better results.
For adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ALL Glivec monotherapy at 600 mg/day is safe, effective and can be given until disease progression occurs.
Posology for Ph+ ALL in children
Dosing for children should be on the basis of body surface area (mg/m²). The dose of 340 mg/m² daily is recommended for children with Ph+ ALL (not to exceed the total dose of 600 mg).
Posology for MDS/MPD
The recommended dose of Glivec is 400 mg/day for adult patients with MDS/MPD.
Treatment duration: In the only clinical trial performed up to now, treatment with Glivec was continued until disease progression (see section 5.1). At the time of analysis, the treatment duration was a median of 47 months (24 days-60 months).
Posology for HES/CEL
The recommended dose of Glivec is 100 mg/day for adult patients with HES/CEL.
Dose increase from 100 mg to 400 mg may be considered in the absence of adverse drug reactions if assessments demonstrate an insufficient response to therapy.
Treatment should be continued as long as the patient continues to benefit.
Posology for GIST
The recommended dose of Glivec is 400 mg/day for adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic malignant GIST.
Limited data exist on the effect of dose increases from 400 mg to 600 mg or 800 mg in patients progressing at the lower dose (see section 5.1).
Treatment duration: In clinical trials in GIST patients, treatment with Glivec was continued until disease progression. At the time of analysis, the treatment duration was a median of 7 months (7 days to 13 months). The effect of stopping treatment after achieving a response has not been investigated.
The recommended dose of Glivec is 400 mg/day for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients following resection of GIST. Optimal treatment duration is not yet established. Length of treatment in the clinical trial supporting this indication was 36 months (see section 5.1).
Posology for DFSP
The recommended dose of Glivec is 800 mg/day for adult patients with DFSP.
Dose adjustment for adverse reactions
Non-haematological adverse reactions
If a severe non-haematological adverse reaction develops with Glivec use, treatment must be withheld until the event has resolved. Thereafter, treatment can be resumed as appropriate depending on the initial severity of the event.
If elevations in bilirubin >3 x institutional upper limit of normal (IULN) or in liver transaminases >5 x IULN occur, Glivec should be withheld until bilirubin levels have returned to <1.5 x IULN and transaminase levels to <2.5 x IULN. Treatment with Glivec may then be continued at a reduced daily dose. In adults the dose should be reduced from 400 to 300 mg or from 600 to 400 mg, or from 800 mg to 600 mg, and in children from 340 to 260 mg/m²/day.
Haematological adverse reactions
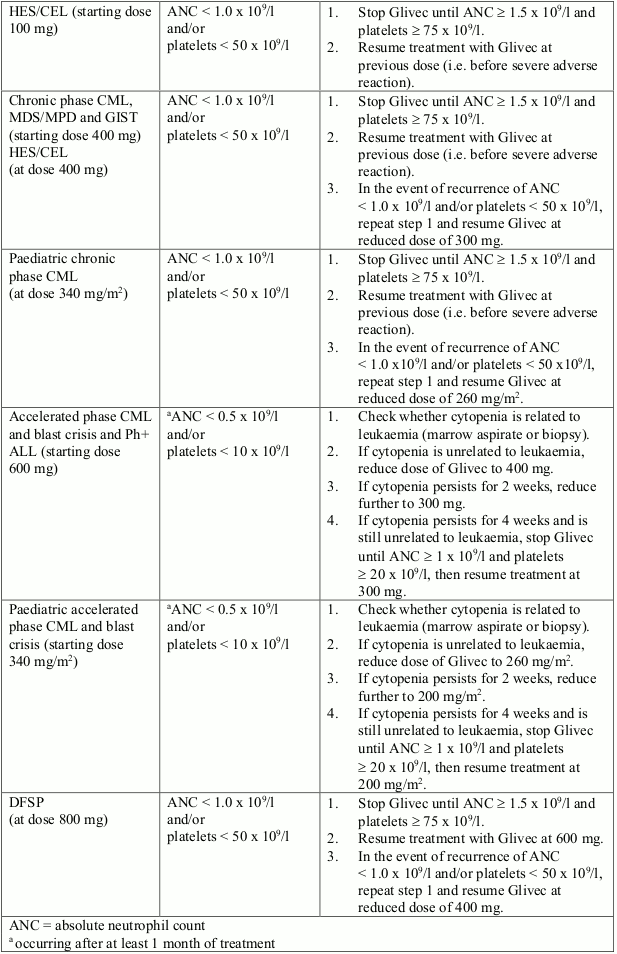
Dose reduction or treatment interruption for severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are recommended as indicated in the table below.
Dose adjustments for neutropenia and thrombocytopenia:
Special populations
Paediatric use
There is no experience in children with CML below 2 years of age and with Ph+ALL below 1 year of age (see section 5.1). There is very limited experience in children with MDS/MPD, DFSP, GIST and HES/CEL.
The safety and efficacy of imatinib in children with MDS/MPD, DFSP, GIST and HES/CEL aged less than 18 years of age have not been established in clinical trials. Currently available published data are summarised in section 5.1 but no recommendation on a posology can be made.
Hepatic insufficiency
Imatinib is mainly metabolised through the liver. Patients with mild, moderate or severe liver dysfunction should be given the minimum recommended dose of 400 mg daily. The dose can be reduced if not tolerated (see sections 4.4, 4.8 and 5.2).
Liver dysfunction classification:
| Liver dysfunction | Liver function tests |
|---|---|
| Mild | Total bilirubin: = 1.5 ULN |
| AST: >ULN (can be normal or <ULN if total bilirubin is >ULN) | |
| Moderate | Total bilirubin: >1.5–3.0 ULN |
| AST: any | |
| Severe | Total bilirubin: >3–10 ULN |
| AST: any |
ULN = upper limit of normal for the institution
AST = aspartate aminotransferase
Renal insufficiency
Patients with renal dysfunction or on dialysis should be given the minimum recommended dose of 400 mg daily as starting dose. However, in these patients caution is recommended. The dose can be reduced if not tolerated. If tolerated, the dose can be increased for lack of efficacy (see sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Older people
Imatinib pharmacokinetics have not been specifically studied in older people. No significant age-related pharmacokinetic differences have been observed in adult patients in clinical trials which included over 20% of patients age 65 and older. No specific dose recommendation is necessary in older people.
Overdose
Experience with doses higher than the recommended therapeutic dose is limited. Isolated cases of Glivec overdose have been reported spontaneously and in the literature. In the event of overdose the patient should be observed and appropriate symptomatic treatment given. Generally the reported outcome in these cases was “improved” or “recovered”. Events that have been reported at different dose ranges are as follows:
Adult population
1200 to 1600 mg (duration varying between 1 to 10 days): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, erythema, oedema, swelling, fatigue, muscle spasms, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, abdominal pain, headache, decreased appetite.
1800 to 3200 mg (as high as 3200 mg daily for 6 days): Weakness, myalgia, increased creatine phosphokinase, increased bilirubin, gastrointestinal pain.
6400 mg (single dose): One case reported in the literature of one patient who experienced nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, facial swelling, decreased neutrophil count, increased transaminases.
8 to 10 g (single dose): Vomiting and gastrointestinal pain have been reported.
Paediatric population
One 3-year-old male exposed to a single dose of 400 mg experienced vomiting, diarrhoea and anorexia and another 3-year-old male exposed to a single dose of 980 mg experienced decreased white blood cell count and diarrhoea.
In the event of overdose, the patient should be observed and appropriate supportive treatment given.
Shelf life
3 years.
Special precautions for storage
Do not store above 30°C.
Store in the original package in order to protect from moisture.
Nature and contents of container
Glivec 100 mg film-coated tablets:
PVC/alu blisters: Packs containing 20, 60, 120 or 180 film-coated tablets.
PVDC/alu blisters: Packs containing 60, 120 or 180 film-coated tablets.
Glivec 400 mg film-coated tablets:
PVDC/alu blisters: Packs containing 10, 30 or 90 film-coated tablets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.