TECOVIRIMAT SIGA Hard capsule Ref.[28350] Active ingredients: Tecovirimat
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2022 Publisher: SIGA Technologies Netherlands B.V., Prinsenhil 29, Breda 4825 AX, The Netherlands
4.3. Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1.
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use
Co-administration of other medicinal products
Co-administration of repaglinide and tecovirimat may cause mild to moderate hypoglycaemia, (see section 4.5). Blood glucose and hypoglycaemic symptoms should be monitored when administering tecovirimat with repaglinide.
Co-administration of midazolam and tecovirimat may reduce the effectiveness of midazolam (see section 4.5). Effectiveness of midazolam should be monitored when administering tecovirimat with midazolam.
Renal impairment
Tecovirimat should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment as there is limited clinical data in this population and higher unbound drug and metabolites levels may be observed. (see sections 4.2 and 5.2).
Hepatic impairment
Tecovirimat should be used with caution in patients with severe hepatic impairment as there is limited clinical data in this population and higher unbound drug and metabolite levels may be observed (see sections 4.2 and 5.2).
Immunocompromised population
The safety and efficacy of tecovirimat has not been evaluated in immunocompromised individuals. Nonclinical studies using animal models indicate that tecovirimat may have reduced efficacy in immunocompromised individuals. (See section 5.1).
Excipients
This medicine contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
This medicine contains sunset yellow (E110). May cause allergic reactions.
4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Effect of other medicinal products on tecovirimat
Tecovirimat is a substrate of UGT1A1, 1A3 and 1A4. Co-administration of tecovirimat with strong inhibitors or inducers of these UGTs is not expected to have a clinically important effect on tecovirimat exposures.
Effect of tecovirimat on other medicinal products
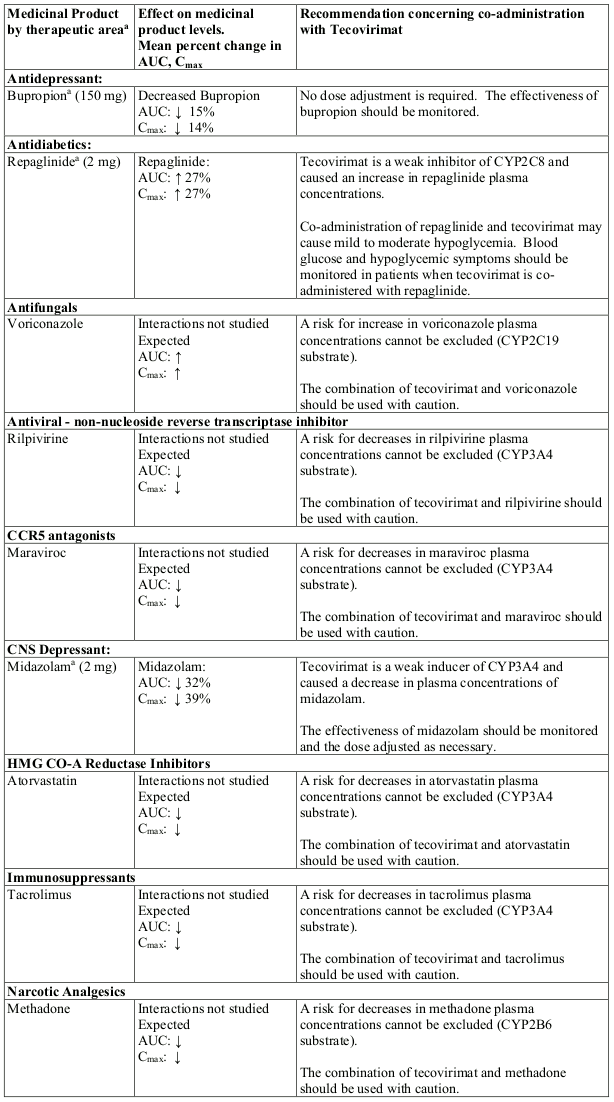
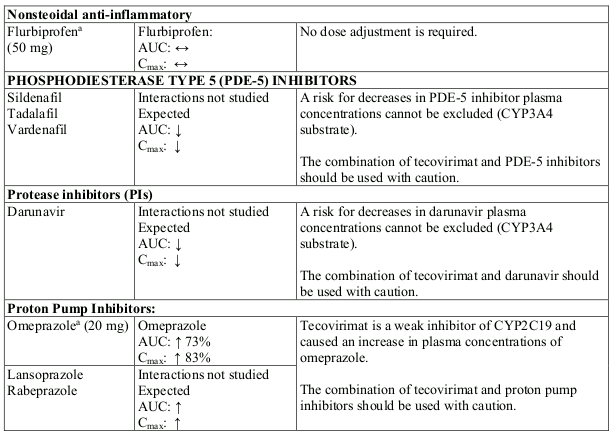
Tecovirimat and its M4 metabolite are inducers of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A and CYP2B6. Co-administration with tecovirimat may lead to reduced plasma exposures of sensitive substrates of CYP3A4 or CYP2B6, potentially leading to reduced effects. Monitoring is advised during co-administration of tecovirimat with CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 substrates that have narrow therapeutic windows. See Table 2 for some examples.
Tecovirimat is a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8 and CYP2C19. Co-administration with tecovirimat may lead to increased plasma exposures of sensitive substrates of CYP2C8 or CYP2C19, potentially leading to increased adverse effects. Monitoring is advised during co-administration of tecovirimat with CYP2C8 and CYP2C19 substrates that have narrow therapeutic windows. See Table 2 for some examples.
Table 2. Interactions and dose recommendations with other medicinal products:
a These interactions have been studied in healthy adults to evaluate the effect of repeated doses of tecovirimat 600 mg twice daily on the single-dose PK of probe substrates.
Vaccine
No vaccine-drug interaction studies have been performed in human subjects. Some animal studies have indicated that co-administration of tecovirimat at the same time as live smallpox vaccine (vaccinia virus) may reduce the immune response to the vaccine.
Paediatric population
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
4.6. Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnancy
There are no data from the use of tecovirimat in pregnant women.
Animal studies are insufficient with respect to reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3).
Tecovirimat is not recommended during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether tecovirimat/metabolites are excreted in human milk.
Available toxicological/safety data in animals have shown excretion of tecovirimat in milk (see section 5.3).
A risk to the newborns/infants cannot be excluded.
Breast-feeding should be discontinued during treatment with tecovirimat.
Fertility
The effects of tecovirimat on fertility in humans have not been studied.
Tecovirimat caused decreased fertility due to testicular toxicity in male mice (see section 5.3).
4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Tecovirimat has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Patients should be informed about the possible occurrence of dizziness and should be cautoned about driving or operating machines until they know how tecovirimat will affect them.
4.8. Undesirable effects
Summary of the safety profile
The most frequently reported adverse drug reactions were headache (12.3%) and nausea (4.5%).
Tabulated summary of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions are classified according to System Organ Class and frequency. Frequency categories are defined as: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000), very rare (<1/10,000) and not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Table 3. Frequency of Adverse Reactions by System Organ Class from Clinical Trials:
| System organ class | Very common | Common | Uncommon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood and lyphatic system disorders | Haematocrit Decreased HaemoglobinDecreased Leucopoenia Thrombocytopenia | ||
| Metabolism and nutrician disorders | Decreased appetite | ||
| Hepatobiliary disorders | Elevated LFT | ||
| Psychiatric disorders | Anxiety Depression Dysphoria Irritability Panic attack | ||
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | Dizziness | Disturbance in attention Dysgeusia Electroencephalogram abnormal Insomnia Migraine Somnolence Paraesthesia |
| Cardiac disorders | Heart Rate Increased Palpitations | ||
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Oropharyngeal pain | ||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Abdominal pain upper Abdominal discomfort Diarrhoea Nausea Vomiting | Abdominal distention Aphthous ulcer Chapped lips Constipation Dry mouth Dyspepsia Eructation Flatulence Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Infrequent bowel movements Paraesthesia oral | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Palpable purpura Pruritus generalised Rash Rash pruritic | ||
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Arthralgia Osteoarthritis | ||
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Chills Fatigue Feeling jittery Malaise Pain Pyrexia Thirst |
Paediatric population
Tecovirimat has not been studied in the paediatric population.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V.
6.2. Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.