YORVIPATH Solution for injection Ref.[51687] Active ingredients: Palopegteriparatide
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2023 Publisher: Ascendis Pharma Bone Diseases A/S, Tuborg Boulevard 12, DK-2900 Hellerup, Denmark
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Yorvipath is a parathyroid hormone (PTH) replacement therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with chronic hypoparathyroidism.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated and monitored by physicians or qualified healthcare professionals experienced in the diagnosis and management of patients with hypoparathyroidism.
Posology
Dose recommendations of Yorvipath refer to micrograms of PTH. The dose should be individualised based on serum calcium. The optimal dose after titration is the minimum dose required to prevent hypocalcaemia. This is the dose that maintains serum calcium within the normal range without the need for active forms of vitamin D or calcium supplementation beyond recommended nutritional supplementation for the general population (generally less than 600 mg per day). Doses of active forms of vitamin D and calcium supplements will need to be adjusted prior to initiating and during treatment with Yorvipath based on serum calcium value (see section 4.4).
Patients receiving the maximum Yorvipath dose of 60 mcg per day who experience ongoing hypocalcaemia may require co-administration of therapeutic calcium and/or active forms of vitamin D.
Before initiation of Yorvipath
Serum 25(OH) vitamin D should be within the normal range and serum calcium should be stable within or slightly below the normal range (1.95-2.64 mmol/L [7.8-10.6 mg/dL]) on at least 1 laboratory value at least two weeks prior to first dose of treatment.
Initiation of Yorvipath
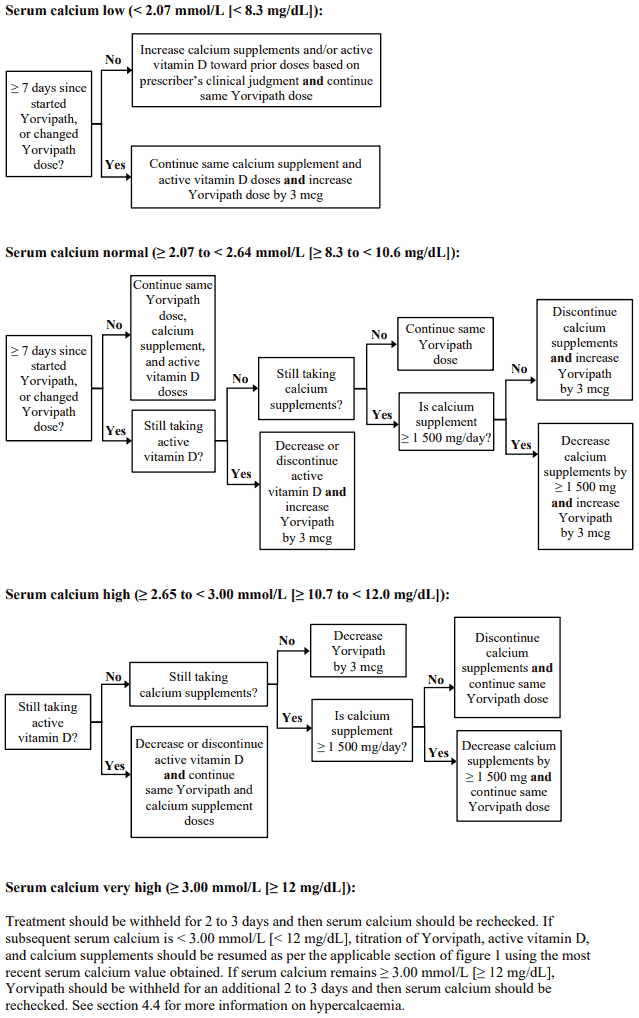
The recommended starting dose is 18 mcg once daily with dose adjustments in 3 mcg increments thereafter every 7 days (see figure 1). The dose range is 6 to 60 mcg per day.
When initiating treatment with Yorvipath, the dose of active vitamin D or calcium supplements should be adjusted:
- If taking active vitamin D:
- If serum calcium is ≥2.07 mmol/L [≥8.3 mg/dL], active vitamin D (calcitriol or alfacalcidol) should be discontinued on the same day as the first dose of Yorvipath. Doses of calcium supplements should be maintained.
- If serum calcium is <2.07 mmol/L [<8.3 mg/dL], active vitamin D should be reduced by ≥50% on the same day as the first dose of Yorvipath. Doses of calcium supplements should be maintained.
- If not taking active vitamin D:
- Calcium supplements should be decreased by at least 1 500 mg on the same day as the first dose of Yorvipath. If taking elemental calcium doses ≤1 500 mg per day, calcium supplements should be discontinued entirely.
- If calcium supplements are indicated to meet dietary requirements, continuing dietary calcium supplements at doses ≤600 mg per day may be considered instead of discontinuing entirely.
Dose adjustment and maintenance of Yorvipath
Serum calcium concentration must be monitored during titration (see section 4.4). Yorvipath dose may be increased in increments of 3 mcg if at least 7 days have elapsed since a prior dose change (see figure 1). The dose must not be increased more often than every 7 days. Yorvipath may be reduced in increments of 3 mcg no more often than every 3 days in response to hypercalcaemia (see figure 1).
Serum calcium should be measured 7 days after the first dose and figure 1 should be followed for appropriate Yorvipath, active vitamin D, and calcium supplement dosing. After any subsequent dose change in Yorvipath, active vitamin D, or calcium supplements, serum calcium should be measured within 7 to 14 days and patients should be monitored for clinical symptoms of hypocalcaemia or hypercalcaemia. Yorvipath, active vitamin D, and/or calcium supplements should be adjusted as per figure 1. Dose adjustments of Yorvipath, active vitamin D, and calcium supplements should be made on the same day.
The maintenance dose should be the dose that achieves serum calcium within the normal range, without the need for active vitamin D or therapeutic doses of calcium. Optionally, calcium supplementation sufficient to meet dietary requirements (≤600 mg per day) may be continued. Serum calcium and 25(OH) vitamin D should be measured as per standard of care when a maintenance dose is achieved. 25(OH) vitamin D (non-active vitamin D) supplementation may be needed to reach normal serum levels.
Figure 1. Titration of Yorvipath, active vitamin D, and calcium supplements:
Missed dose
If a dose is missed by less than 12 hours, it should be administered as soon as possible. If a dose is missed by more than 12 hours, it should be skipped and the next dose should be administered as scheduled.
Interruption or discontinuation of Yorvipath
Interruption of daily administration should be avoided to minimise serum PTH fluctuations. Interruption or discontinuation of treatment can result in hypocalcaemia. When interrupting or discontinuing treatment for 3 or more consecutive doses, patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of hypocalcaemia and consider to measure serum calcium. If indicated, treatment with calcium supplements and active vitamin D should be resumed. Treatment at the prescribed dose should be resumed as soon as possible after an interruption. When resuming treatment after an interruption, serum calcium should be measured and doses of Yorvipath, active vitamin D, and calcium supplements should be adjusted as per figure 1.
Special populations
Elderly
Dose adjustment is not required based on age (see section 5.2).
Hepatic impairment
Yorvipath has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and should be used with caution in these patients (see section 4.4).
Renal impairment
Dose adjustment is not required in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥30 mL/min. Serum calcium levels should be measured more frequently when used in patients with eGFR <45 mL/min (see section 4.4). Yorvipath has not been studied in patients with hypoparathyroidism and severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min) (see section 5.2).
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Yorvipath in children less than 18 years of age have not yet been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Yorvipath must be administered as a subcutaneous injection to the abdomen or front of the thigh. The injection site should be rotated daily between four possible sites; abdomen (left or right) and front of the thigh (left or right).
Doses >30 mcg per day (sequential injections)
All doses >30 mcg per day should be administered as two single doses injected sequentially at different injection sites (table 1). It is recommended to use a different Yorvipath pen for the second daily injection, even if the two pens have the same-coloured push button (same strength).
Table 1. Recommended scheme for Yorvipath dosing >30 mcg/day:
| Dose | Dosing scheme | Pen combination |
|---|---|---|
| 33 mcg/day | 15 mcg/day + 18 mcg/day | Two pre-filled pens of Yorvipath 294 mcg/0.98 mL (orange push button)* |
| 36 mcg/day | 18 mcg/day + 18 mcg/day | |
| 39 mcg/day | 18 mcg/day + 21 mcg/day | |
| 42 mcg/day | 21 mcg/day + 21 mcg/day | |
| 45 mcg/day | 21 mcg/day + 24 mcg/day | One pre-filled pen of Yorvipath 294 mcg/0.98 mL (orange push button) + One pre-filled pen of Yorvipath 420 mcg/1.4 mL (burgundy push button)** |
| 48 mcg/day | 24 mcg/day + 24 mcg/day | Two pre-filled pens of Yorvipath 420 mcg/1.4 mL (burgundy push button) |
| 51 mcg/day | 24 mcg/day + 27 mcg/day | |
| 54 mcg/day | 27 mcg/day + 27 mcg/day | |
| 57 mcg/day | 27 mcg/day + 30 mcg/day | |
| 60 mcg/day | 30 mcg/day + 30 mcg/day |
* Yorvipath 294 micrograms/0.98 mL delivers doses of 15, 18, or 21 mcg of PTH (with orange push button)
** Yorvipath 420 micrograms/1.4 mL delivers doses of 24, 27, or 30 mcg of PTH (with burgundy push button)
4.9. Overdose
In the event of overdose, the patient should be carefully monitored by a medical professional.
Overdose can cause hypercalcaemia, the manifestations of which may include dehydration, heart palpitations, ECG changes, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, muscle weakness, and confusion. Severe hypercalcaemia may require medical care and careful monitoring (see section 4.4).
One instance of accidental overdose of approximately 3-fold the prescribed dose lasting more than 7 consecutive days resulted in serum calcium as high as 16.1 mg/dL, the patient was symptomatic and required medical intervention. After withholding palopegteriparatide, calcium, and active vitamin D, the patient recovered and restarted on the correct dose.
6.3. Shelf life
3 years.
After first opening:
Store below 30°C.
Keep the pen cap on the pre-filled pen in order to protect from light.
Yorvipath must be discarded after 14 days.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package with the pen cap on in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions after first opening of the medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
A cartridge (type 1 glass) with a plunger (halobutyl) and a laminate rubber sheet (halobutyl/isoprene) contained in a pre-filled multidose disposable pen made of polypropylene.
Packs of two pre-filled pens and 30 disposable needles for 28 days of treatment (co-packaged in two inner cartons). Each inner carton contains one pre-filled pen and 15 needles for 14 days of treatment.
Yorvipath 168 micrograms/0.56 mL solution for injection in pre-filled pen:
- Each pre-filled pen contains palopegteriparatide equivalent to 168 micrograms of PTH in 0.56 mL of solvent.
- Pre-filled pen delivering doses of 6, 9, or 12 micrograms.
- The strength colour on the outer carton, pen label and push button is blue.
Yorvipath 294 micrograms/0.98 mL solution for injection in pre-filled pen:
- Each pre-filled pen contains palopegteriparatide equivalent to 294 micrograms of PTH in 0.98 mL of solvent.
- Pre-filled pen, delivering doses of 15, 18, or 21 micrograms.
- The strength colour on the outer carton, pen label and push button is orange.
Yorvipath 420 micrograms/1.4 mL solution for injection in pre-filled pen:
- Each pre-filled pen contains palopegteriparatide equivalent to 420 micrograms of PTH in 1.4 mL of solvent.
- Pre-filled pen, delivering doses of 24, 27, or 30 micrograms.
- The strength colour on the outer carton, pen label and push button is burgundy.
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Dose preparation
A new Yorvipath pen should be taken out of the refrigerator 20 minutes before first opening.
The solution should appear clear, colourless and free of visible particles. Do not inject the medicinal product if it is cloudy, or contains particulate matter.
Each pre-filled pen is for use by a single patient. A pre-filled pen must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed.
If a pre-filled pen has been frozen or exposed to heat, it must be discarded.
Every time a pre-filled pen is prepared for administration, a new needle must be attached.
Needles must not be re-used. This may prevent blocked needles, contamination, infection, leakage of solution and inaccurate dosing. The injection needle should be removed after each injection and the pen should be stored without a needle attached. Discard the needles after each injection.
Instructions for the preparation and administration of Yorvipath are given in the package leaflet and instructions for use.
Disposal
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.