TEKTURNA Film-coated tablet Ref.[50359] Active ingredients: Aliskiren
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2021
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Renin is secreted by the kidney in response to decreases in blood volume and renal perfusion. Renin cleaves angiotensinogen to form the inactive decapeptide angiotensin I (Ang I). Ang I is converted to the active octapeptide angiotensin II (Ang II) by ACE and non-ACE pathways. Ang II is a powerful vasoconstrictor and leads to the release of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla and prejunctional nerve endings. It also promotes aldosterone secretion and sodium reabsorption. Together, these effects increase blood pressure. Ang II also inhibits renin release, thus providing a negative feedback to the system. This cycle, from renin through angiotensin to aldosterone and its associated negative feedback loop, is known as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Aliskiren is a direct renin inhibitor, decreasing plasma renin activity (PRA) and inhibiting the conversion of angiotensinogen to Ang I. Whether aliskiren affects other RAAS components, e.g., ACE or non-ACE pathways, is not known.
All agents that inhibit the RAAS, including renin inhibitors, suppress the negative feedback loop, leading to a compensatory rise in plasma renin concentration. When this rise occurs during treatment with ACEIs and ARBs, the result is increased levels of PRA. During treatment with aliskiren, however, the effect of increased renin levels is blocked so that PRA, Ang I and Ang II are all reduced, whether aliskiren is used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
12.2. Pharmacodynamics
In placebo-controlled clinical trials, PRA was decreased in a range of 50% to 80%. This reduction in PRA was not dose- related and did not correlate with blood pressure reductions. The clinical implications of the differences in effect on PRA are not known.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Aliskiren is poorly absorbed (bioavailability about 2.5%) with an approximate accumulation half-life of 24 hours. Steady state blood levels are reached in about 7 to 8 days.
Absorption and Distribution
Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations of aliskiren are reached within 1 to 3 hours. When taken with a high-fat meal, mean AUC and Cmax of aliskiren are decreased by 71% and 85% respectively. In the clinical trials of aliskiren, it was administered without requiring a fixed relation of administration to meals.
Metabolism and Elimination
About one-fourth of the absorbed dose appears in the urine as parent drug. How much of the absorbed dose is metabolized is unknown. Based on the in vitro studies, the major enzyme responsible for aliskiren metabolism appears to be CYP3A4. Aliskiren does not inhibit the CYP450 isoenzymes (CYP 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A) or induce CYP3A4.
Transporters
Pgp (MDR1/Mdr1a/1b) was found to be the major efflux system involved in intestinal absorption and elimination via biliary excretion of aliskiren in preclinical studies. The potential for drug interactions at the Pgp site will likely depend on the degree of inhibition of this transporter.
Drug Interactions
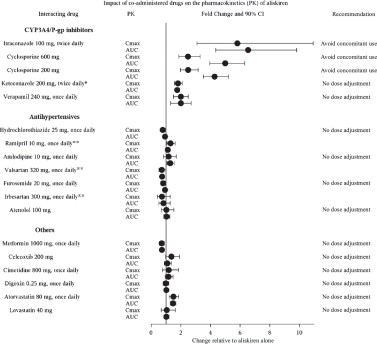
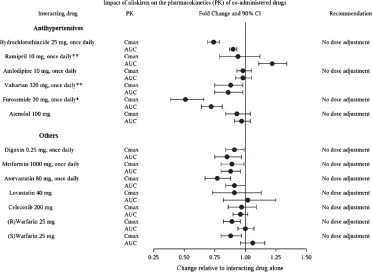
The effect of coadministered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren and vice versa, were studied in several single- and multiple-dose studies. Pharmacokinetic measures indicating the magnitude of these interactions are presented in Figure 1 (impact of coadministered drugs on aliskiren) and Figure 2 (impact of aliskiren on coadministered drugs).
Figure 1. The Impact of Coadministered Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Aliskiren:
* Ketoconazole: A 400 mg once daily dose was not studied, but would be expected to increase aliskiren blood levels further.
** Ramipril, valsartan, irbesartan: In general, avoid combined use of aliskiren with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, particularly in patients with CrCl less than 60 mL/min [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Warfarin: There was no clinically significant effect of a single dose of warfarin 25 mg on the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren.
Figure 2. The Impact of Aliskiren on the Pharmacokinetics of Coadministered Drugs:
* Furosemide: Patients receiving furosemide could find its effects diminished after starting aliskiren. In patients with heart failure, coadministration of aliskiren (300 mg/day) reduced plasma AUC and Cmax of oral furosemide (60 mg/day) by 17% and 27%, respectively, and reduced 24-hour urinary furosemide excretion by 29%. This change in exposure did not result in statistically significant difference in total urine volume and urinary sodium excretion over 24 hours. However, a transient decrease in urinary sodium excretion and urine volume effects up to 12 hours were observed when furosemide was coadministered with aliskiren 300 mg/day.
** Ramipril, valsartan: In general, avoid combined use of aliskiren with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, particularly in patients with CrCl less than 60 mL/min [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Specific Populations
Renally Impaired Patients
Aliskiren was evaluated in adult patients with varying degrees of renal insufficiency. The rate and extent of exposure (AUC and Cmax) of aliskiren in subjects with renal impairment did not show a consistent correlation with the severity of renal impairment. Adjustment of the starting dose is not required in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren following administration of a single oral dose of 300 mg was evaluated in adult patients with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis. When compared to matched healthy subjects, changes in the rate and extent of aliskiren exposure (Cmax and AUC) in ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis were not clinically significant.
Timing of hemodialysis did not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren in ESRD patients. Therefore, no dose adjustment is warranted in ESRD patients receiving hemodialysis.
Hepatically Impaired Patients
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren were not significantly affected in patients with mild to severe liver disease. Consequently, adjustment of the starting dose is not required in these patients.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren were evaluated in an 8-day pharmacokinetic study in 39 pediatric patients with hypertension 6 years to 17 years of age. Aliskiren was given as daily doses of 2 mg/kg (0.67 times the lowest approved recommended dosage in a 50 kg pediatric patient) or 6 mg/kg (the highest recommended approved dosage in a 50 kg pediatric patient), administered as mini-tablets (3.125 mg oral pellets). The pharmacokinetic parameters of aliskiren were similar to those in adults, and the results of this study do not suggest that age or gender have any significant effect on aliskiren systemic exposure in patients 6 years to 17 years of age. Exposure decreased with increase in body weight.
In an 8-week randomized double blind study with aliskiren monotherapy in 267 pediatric patients with hypertension 6 years to 17 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.4)], fasting trough aliskiren concentrations at Day 28 demonstrated similar drug trough exposure levels to those observed in other trials using similar aliskiren doses in both adults and pediatric patients.
Geriatric Patients
Exposure (measured by AUC) is increased in elderly patients 65 years and older. Adjustment of the starting dose is not required in these patients.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
The pharmacokinetic differences between blacks, Caucasians, and Japanese are minimal.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenic potential was assessed in a 2-year rat study and a 6-month transgenic (rasH2) mouse study with aliskiren hemifumarate at oral doses of up to 1500 mg aliskiren/kg/day. Although there were no statistically significant increases in tumor incidence associated with exposure to aliskiren, mucosal epithelial hyperplasia (with or without erosion/ulceration) was observed in the lower gastrointestinal tract at doses of greater than or equal to 750 mg/kg/day in both species, with a colonic adenoma identified in 1 rat and a cecal adenocarcinoma identified in another, rare tumors in the strain of rat studied. On a systemic exposure (AUC0-24hr) basis, 1500 mg/kg/day in the rat is about 4 times and in the mouse about 1.5 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (300 mg aliskiren/day). Mucosal hyperplasia in the cecum or colon of rats was also observed at doses of 250 mg/kg/day (the lowest tested dose) as well as at higher doses in 4- and 13-week studies.
Aliskiren hemifumarate was devoid of genotoxic potential in the Ames reverse mutation assay with S. typhimurium and E. coli, the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosomal aberration assay, the in vitro Chinese hamster V79 cell gene mutation test and the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility of male and female rats was unaffected at doses of up to 250 mg aliskiren/kg/day (8 times the MRHD of 300 mg Tekturna/60 kg on a mg/m² basis.)
13.2. Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproductive Toxicology Studies
Reproductive toxicity studies of aliskiren hemifumarate did not reveal any evidence of teratogenicity at oral doses up to 600 mg aliskiren/kg/day (20 times the MRHD of 300 mg/day on a mg/m² basis) in pregnant rats or up to 100 mg aliskiren/kg/day (7 times the MRHD on a mg/m² basis) in pregnant rabbits. Fetal birth weight was adversely affected in rabbits at 50 mg/kg/day (3.2 times the MRHD on a mg/m² basis). Aliskiren was present in placenta, amniotic fluid and fetuses of pregnant rabbits.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Aliskiren Monotherapy
The antihypertensive effects of Tekturna have been demonstrated in 6 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 8- week clinical trials in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. The placebo response and placebo-subtracted changes from baseline in seated trough cuff blood pressure are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Reductions in Seated Trough Cuff Blood Pressure (mmHg systolic/diastolic) in the Placebo-Controlled Studies:
| Aliskiren daily dose, mg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Placebo mean change | 75 | 150 | 300 | 600 |
| Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | ||
| 1 | 2.9/3.3 | 5.7/4* | 5.9/4.5* | 11.2/7.5 * | -- |
| 2 | 5.3/6.3 | -- | 6.1/2.9* | 10.5/5.4* | 10.4/5.2* |
| 3 | 10/8.6 | 2.2/1.7 | 2.1/1.7 | 5.1/3.7* | -- |
| 4 | 7.5/6.9 | 1.9/1.8 | 4.8/2* | 8.3/3.3* | -- |
| 5 | 3.8/4.9 | -- | 9.3/5.4* | 10.9/6.2* | 12.1/7.6* |
| 6 | 4.6/4.1 | -- | -- | 8.4/4.9† | -- |
* p value less than 0.05 versus placebo by ANCOVA with Dunnett’s procedure for multiple comparisons
† p value less than 0.05 versus placebo by ANCOVA for the pairwise comparison.
The studies included approximately 2,730 patients given doses of 75 mg (0.5 times the lowest recommended dosage) to 600 mg (twice the highest recommended dosage) of aliskiren and 1,231 patients given placebo. The recommended dosage of Tekturna is either 150 or 300 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. As shown in Table 1, there is some increase in response with administered dose in all studies, with reasonable effects seen at 150mg to 300 mg, and no clear further increases at 600 mg. A substantial proportion (85% to 90%) of the blood pressure-lowering effect was observed within 2 weeks of treatment. Studies with ambulatory blood pressure monitoring showed reasonable control throughout the interdosing interval; the ratios of mean daytime to mean nighttime ambulatory BP range from 0.6 to 0.9.
Patients in the placebo-controlled trials continued open-label aliskiren for up to 1 year. A persistent blood pressure- lowering effect was demonstrated by a randomized withdrawal study (patients randomized to continue drug or placebo), which showed a statistically significant difference between patients kept on aliskiren and those randomized to placebo. With cessation of treatment, blood pressure gradually returned toward baseline levels over a period of several weeks.
There was no evidence of rebound hypertension after abrupt cessation of therapy.
Aliskiren lowered blood pressure in all demographic subgroups, although black patients tended to have smaller reduction than Caucasians and Asians, as has been seen with ACEIs and ARBs.
There are no studies of Tekturna or members of the direct renin inhibitors demonstrating reductions in cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension.
14.2 Aliskiren in Combination with Other Antihypertensives
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
Aliskiren 75, 150, and 300 mg (0.5 times the recommended lowest dosage, the lowest recommended dosage, and the maximum recommended dosage, respectively) and HCTZ 6.25, 12.5, and 25 mg were studied alone and in combination in an 8-week, 2,776-patient, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, 15-arm factorial study. Blood pressure reductions with the combinations were greater than the reductions with the monotherapies as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Placebo-Subtracted Reductions in Seated Trough Cuff Blood Pressure (mmHg systolic/diastolic) in Combination with Hydrochlorothiazide:
| Hydrochlorothiazide, mg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aliskiren, mg | Placebo mean change | 0 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 25 |
| Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | Placebo-subtracted | ||
| 0 | 7.5/6.9 | -- | 3.5/2.1 | 6.4/3.2 | 6.8/2.4 |
| 75 | -- | 1.9/1.8 | 6.8/3.8 | 8.2/4.2 | 9.8/4.5 |
| 150 | -- | 4.8/2 | 7.8/3.4 | 10.1/5 | 12/5.7 |
| 300 | -- | 8.3/3.3 | -- | 12.3/7 | 13.7/7.3 |
Valsartan
Aliskiren 150 mg and 300 mg and valsartan 160 mg and 320 mg were studied alone and in combination in an 8-week, 1,797-patient, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, 4-arm, dose-escalation study. The dosages of aliskiren and valsartan were started at 150 mg and 160 mg, respectively, and increased at 4 weeks to 300 mg and 320 mg, respectively. Seated trough cuff blood pressure was measured at baseline, 4, and 8 weeks. Blood pressure reductions with the combinations were greater than the reductions with the monotherapies as shown in Table 4. In general, the combination of aliskiren and angiotensin receptor blocker should be avoided [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5), and Drug Interactions (7)].
Table 4. Placebo-Subtracted Reductions in Seated Trough Cuff Blood Pressure (mmHg systolic/diastolic) in Combination with Valsartan:
| Aliskiren, mg | Placebo mean change | Valsartan, mg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 160 | 320 | ||
| 0 | 4.6/4.1* | -- | 5.6/3.9 | 8.2/5.6 |
| 150 | -- | 5.4/2.7 | 10.0/5.7 | -- |
| 300 | -- | 8.4/4.9 | -- | 12.6/8.1 |
* The placebo change is 5.2/4.8 for week 4 endpoint which was used for the dose groups containing aliskiren 150 mg or valsartan 160 mg.
Amlodipine
Aliskiren 150 mg and 300 mg and amlodipine besylate 5 mg and 10 mg were studied alone and in combination in an 8- week, 1,685-patient, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multifactorial study. Treatment with aliskiren and amlodipine resulted overall in significantly greater reductions in diastolic and systolic blood pressure compared to the respective monotherapy components as shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Placebo-Subtracted Reductions in Seated Trough Cuff Blood Pressure (mmHg systolic/diastolic) in Combination with Amlodipine:
| Aliskiren, mg | Placebo mean change | Amlodipine, mg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | ||
| 0 | 6.8/5.4 | -- | 9.0/5.6 | 14.3/8.5 |
| 150 | -- | 3.9/2.6 | 13.9/8.6 | 17.1/10.8 |
| 300 | -- | 8.6/4.9 | 15.0/9.6 | 16.4/11.1 |
14.3 Aliskiren in Patients with Diabetes Treated with ARB or ACEI (ALTITUDE study)
Patients with diabetes with renal disease (defined either by the presence of albuminuria or reduced GFR) were randomized to aliskiren 300 mg daily (n=4296) or placebo (n=4310). All patients were receiving background therapy with an ARB or ACEI. The primary efficacy outcome was the time to the first event of the primary composite endpoint consisting of cardiovascular death, resuscitated sudden death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, unplanned hospitalization for heart failure, onset of end stage renal disease, renal death, and doubling of serum creatinine concentration from baseline sustained for at least 1 month. After a median follow-up of about 32 months, the trial was terminated early for lack of efficacy. Higher risk of renal impairment, hypotension and hyperkalemia was observed in aliskiren compared to placebo-treated patients, as shown in Table 6.
Table 6. Incidence of Selected Adverse Events During the Treatment Phase in ALTITUDE:
| Aliskiren N=4272 | Placebo N=4285 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serious Adverse Events* (%) | Adverse Events (%) | Serious Adverse Events* (%) | Adverse Events (%) | |
| Renal impairment† | 5.7 | 14.5 | 4.3 | 12.4 |
| Hypotension†† | 2.3 | 19.9 | 1.9 | 16.3 |
| Hyperkalemia††† | 1.0 | 38.9 | 0.5 | 28.8 |
† renal failure, renal failure acute, renal failure chronic, renal impairment
†† dizziness, dizziness postural, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, presyncope, syncope
††† Given the variable baseline potassium levels of patients with renal insufficiency on dual RAAS therapy, the reporting of adverse event of hyperkalemia was at the discretion of the investigator.
* A Serious Adverse Event (SAE) is defined as: an event which is fatal or life-threatening, results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity, constitutes a congenital anomaly/birth defect, requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization, or is medically significant (i.e., defined as an event that jeopardizes the patient or may require medical or surgical intervention to prevent one of the outcomes previously listed).
The risk of stroke (3.4% aliskiren versus 2.7% placebo) and death (8.4% aliskiren versus 8.0% placebo) were also numerically higher in aliskiren treated patients.
14.4 Pediatric Hypertension
The efficacy of aliskiren was evaluated in an 8-week randomized, double-blind trial in 267 pediatric patients with hypertension 6 years to 17 years of age (Study CSPP100A2365; NCT01150357). The majority of patients (82%) had primary hypertension, 59% had a BMI ≥95 th percentile, 20% had an estimated GFR between 60 and 90 mL/min/1.73m² and <2% had an estimated GFR <60 mL/min/1.73m². The mean age was 11.8 years and 74% of patients were Caucasian. In the initial 4-week,dose-response phase of the trial patients were randomized to weight-based low, mid and high dosing groups. At the end of this phase, patients entered a 4-week randomized withdrawal phase in which they were re-randomized in each weight category in a 1:1 ratio to continue the same dose of aliskiren or take placebo.
During the initial dose-response phase, aliskiren reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a weight-based dose-dependent manner. Sitting systolic blood pressure, the trial’s primary endpoint, was reduced by 4.8, 5.6 and 8.7 mmHg from baseline in the low, medium and high dose groups, respectively. In the randomized withdrawal phase, the mean difference between the high dose group of aliskiren and placebo in the mean change in sitting systolic blood pressure was -2.7 mmHg.
Following the 8-week trial, 208 patients were enrolled in a 52-week extension trial in which patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio (irrespective of whether they were on placebo or aliskiren at the end of the 8-week study) to receive either aliskiren or enalapril (CSPP100A2365E1; NCT01151410). The extension study included 3 dose levels based on weight; optional dose up-titrations were allowed during the study to control blood pressure.
At the end of 52 weeks, reductions in blood pressure from baseline were similar in patients receiving aliskiren (7.6/3.9 mmHg) and enalapril (7.9/4.9 mmHg).
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.